Journal Description
Biology
Biology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of biological sciences published monthly online by MDPI. The Spanish Society for Nitrogen Fixation (SEFIN) and Federation of European Laboratory Animal Science Associations (FELASA) are affiliated with Biology, and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, PubAg, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Biology) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Agricultural and Biological Sciences)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Companion journal: Foundations.
Impact Factor:
4.2 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.4 (2022)
Latest Articles
Multi-Probe RFA vs. Single-Probe MWA in an Ex Vivo Bovine Liver Model: Comparison of Volume and Shape of Coagulation Zones
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1103; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081103 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the volumes and shapes of the coagulation zone (CZ) of a multi-probe RFA system (three RFA electrodes) and a single-probe MWA system from the same vendor in an ex vivo bovine liver model. Material & Methods: A total of 48
[...] Read more.
Objectives: To compare the volumes and shapes of the coagulation zone (CZ) of a multi-probe RFA system (three RFA electrodes) and a single-probe MWA system from the same vendor in an ex vivo bovine liver model. Material & Methods: A total of 48 CZs were obtained in bovine liver specimens with three different ablation system configurations (single-probe MWA vs. multi-probe RFA with 20 mm inter-probe distance [confluent CZ] vs. multi-probe RFA with 50 mm inter-probe distance [three individual CZs]) at 4, 6, 8, and 10 min ablation time using a fixed ablation protocol. Ablation diameters were measured and ellipticity indices (EIs) and volumes calculated. Calculations for all systems/configurations were compared. Results: Volumes and diameters increased with ablation time for all configurations. At 4 and 6 min ablation time volumes obtained with the RFA 50 mm setup, and at 8 and 10 min with the RFA 20 mm setup were the largest at 26.5 ± 4.1 mL, 38.1 ± 5.8 mL, 46.3 ± 4.9 mL, 48.4 ± 7.3 mL, respectively. The single-probe MWA could not reach the volumes of the RFA setups for any of the ablation times evaluated. EI were very similar and almost round for RFA 20 mm and single-probe MWA, and differed significantly to the more ovoid ones for the RFA 50 mm configuration. Conclusion: The multi-probe RFA system employing three electrodes achieved significantly larger ablation volumes in both configurations (confluent CZ and three individual CZs) per time as compared with a single-probe MWA system in this ex vivo bovine liver model.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Understanding of Cellular Changes in Liver Pathophysiology)
Open AccessCommunication
The Stochastic Nature Exhibited by Proteins inside the Cell Membrane during Cell-to-Cell Communication
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1102; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081102 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The movement of proteins through the cell membrane is essential for cell-to-cell communication, which is a process that allows the body’s immune system to identify any foreign cells, such as cells from another organism and pathogens; this movement is also essential for protein-to-protein
[...] Read more.
The movement of proteins through the cell membrane is essential for cell-to-cell communication, which is a process that allows the body’s immune system to identify any foreign cells, such as cells from another organism and pathogens; this movement is also essential for protein-to-protein interactions and protein-to-membrane interactions which play a significant role in drug discovery. This paper presents the stochastic nature exhibited by proteins during cell-to-cell communication. We study the movement of proteins through the cell membrane under the influence of an external force F and drag force with drag coefficient
(This article belongs to the Section Cell Biology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cuproptosis- and m6A-Related lncRNAs for Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1101; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081101 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Cuproptosis and N6-methyladenosine (m6A) have potential as prognostic predictors in cancer patients, but their roles in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are unclear. This study aimed to screen a total of 375 HCC samples were retrieved from the TCGA database, and lncRNAs related to cuproptosis
[...] Read more.
Cuproptosis and N6-methyladenosine (m6A) have potential as prognostic predictors in cancer patients, but their roles in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are unclear. This study aimed to screen a total of 375 HCC samples were retrieved from the TCGA database, and lncRNAs related to cuproptosis and m6A were obtained through correlation analysis. To construct a risk assessment model, univariate Cox regression analysis and LASSO Cox regression were employed. Analyze the regulatory effect of relevant risk assessment models on tumor mutation load (TMB) and immune microenvironment. A total of five lncRNAs (AC007405.3, AL031985.3, TMCC1-AS1, MIR210HG, TMEM220-AS1) with independent overall survival-related risk models were obtained by LASSO survival regression. TP53 and CTNNB1 were the three genes found to have the most mutations in high-risk group patients. The high-risk group with low TMB had the worst survival, whereas the low-risk group with high TMB had the best survival. KEGG pathway analysis revealed that the high-risk group was enriched with cell cycle, oocyte meiosis, cell senescence, and glycolysis/glucose production pathways. We constructed a reliable cuproptosis- and m6A-related lncRNA model for the prognosis of HCC. The model may provide new insights into managing HCC patients, but further research is needed to validate it.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioinformatics and Machine Learning for Cancer Biology (Volume II))
►▼
Show Figures
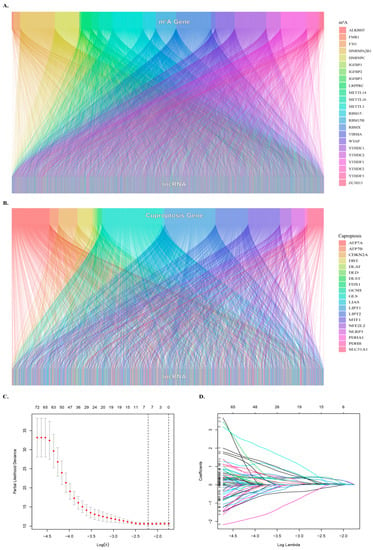
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
LPS-Induced Garcia Effect and Its Pharmacological Regulation Mediated by Acetylsalicylic Acid: Behavioral and Transcriptional Evidence
by
, , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1100; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081100 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
Lymnaea stagnalis learns and remembers to avoid certain foods when their ingestion is followed by sickness. This rapid, taste-specific, and long-lasting aversion—known as the Garcia effect—can be formed by exposing snails to a novel taste and 1 h later injecting them with lipopolysaccharide
[...] Read more.
Lymnaea stagnalis learns and remembers to avoid certain foods when their ingestion is followed by sickness. This rapid, taste-specific, and long-lasting aversion—known as the Garcia effect—can be formed by exposing snails to a novel taste and 1 h later injecting them with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). However, the exposure of snails to acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) for 1 h before the LPS injection, prevents both the LPS-induced sickness state and the Garcia effect. Here, we investigated novel aspects of this unique form of conditioned taste aversion and its pharmacological regulation. We first explored the transcriptional effects in the snails’ central nervous system induced by the injection with LPS (25 mg), the exposure to ASA (900 nM), as well as their combined presentation in untrained snails. Then, we investigated the behavioral and molecular mechanisms underlying the LPS-induced Garcia effect and its pharmacological regulation by ASA. LPS injection, both alone and during the Garcia effect procedure, upregulated the expression levels of immune- and stress-related targets. This upregulation was prevented by pre-exposure to ASA. While LPS alone did not affect the expression levels of neuroplasticity genes, its combination with the conditioning procedure resulted in their significant upregulation and memory formation for the Garcia effect.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Neurobiology of Invertebrates Inaccessible from Mammalian Studies)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Extracellular Vesicles in Pulmonary Hypertension: A Dangerous Liaison?
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1099; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081099 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
The term pulmonary hypertension (PH) refers to different conditions, all characterized by increased pressure and resistance in the pulmonary arterial bed. PH has a wide range of causes (essentially, cardiovascular, pulmonary, or connective tissue disorders); however, idiopathic (i.e., without a clear cause) PH
[...] Read more.
The term pulmonary hypertension (PH) refers to different conditions, all characterized by increased pressure and resistance in the pulmonary arterial bed. PH has a wide range of causes (essentially, cardiovascular, pulmonary, or connective tissue disorders); however, idiopathic (i.e., without a clear cause) PH exists. This chronic, progressive, and sometimes devastating disease can finally lead to right heart failure and eventually death, through pulmonary vascular remodeling and dysfunction. The exact nature of PH pathophysiology is sometimes still unclear. Extracellular vesicles (EVs), previously known as apoptotic bodies, microvesicles, and exosomes, are small membrane-bound vesicles that are generated by almost all cell types and can be detected in a variety of physiological fluids. EVs are involved in intercellular communication, thus influencing immunological response, inflammation, embryogenesis, aging, and regenerative processes. Indeed, they transport chemokines, cytokines, lipids, RNA and miRNA, and other biologically active molecules. Although the precise functions of EVs are still not fully known, there is mounting evidence that they can play a significant role in the pathophysiology of PH. In this review, after briefly recapping the key stages of PH pathogenesis, we discuss the current evidence on the functions of EVs both as PH biomarkers and potential participants in the distinct pathways of disease progression.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Extracellular Vesicles from Health to Disease: Positive or Negative Benefits)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Fungal Root Endophyte Serendipita indica (Piriformospora indica) Enhances Bread and Durum Wheat Performance under Boron Toxicity at Both Vegetative and Generative Stages of Development through Mechanisms Unrelated to Mineral Homeostasis
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1098; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081098 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
While the importance of beneficial soil microorganisms for soil health and crop performance has been receiving ever-increasing attention, Serendipita indica has been widely studied as a fungal root endophyte with significant potential for increasing the stress tolerance of host plants. Boron (B) toxicity
[...] Read more.
While the importance of beneficial soil microorganisms for soil health and crop performance has been receiving ever-increasing attention, Serendipita indica has been widely studied as a fungal root endophyte with significant potential for increasing the stress tolerance of host plants. Boron (B) toxicity as an adverse soil condition is particularly prevalent in arid and semi-arid regions and threatens crop production. Studies on S. indica-wheat symbiosis are limited, and effects of S. indica on crops have never been reported in the context of B toxicity. Here, two pot experiments were conducted under greenhouse conditions to investigate the effects of S. indica on the growth and yield parameters of bread (Triticum aestivum) and durum wheat (Triticum durum) grown at different levels of B toxicity in native vs. sterilized soil, and parameters related to root colonization, membrane damage, oxidative stress, chlorophyll, and mineral nutrition were measured to elucidate the physiological mechanisms of damage and benefit. Boron toxicity decreased early vegetative growth and grain yield, but it did not affect the straw dry weight of mature plants, whereas S. indica significantly enhanced the vegetative growth, straw dry weight, and the grain number of both wheat species. Membrane damage as demonstrated by increased lipid peroxidation and relative electrolyte leakage was caused by B toxicity and alleviated by S. indica. The benefits provided by S. indica could not be attributed to any significant changes in tissue concentrations of B or other minerals such as phosphorus. Soil sterilization generally improved plant performance but it did not consistently strengthen or weaken the effects of S. indica. The presented results suggest that S. indica may be used as an effective microbial inoculant to enhance wheat growth under adverse soil conditions such as B toxicity through mechanisms that are possibly unrelated to mineral homeostasis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mechanism of Interaction between Rhizosphere Microbes and Host Plants)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mid-Pleistocene Transitions Forced Himalayan ibex to Evolve Independently after Split into an Allopatric Refugium
by
, , , , , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1097; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081097 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
Pleistocene glaciations had profound impact on the spatial distribution and genetic makeup of species in temperate ecosystems. While the glacial period trapped several species into glacial refugia and caused abrupt decline in large populations, the interglacial period facilitated population growth and range expansion
[...] Read more.
Pleistocene glaciations had profound impact on the spatial distribution and genetic makeup of species in temperate ecosystems. While the glacial period trapped several species into glacial refugia and caused abrupt decline in large populations, the interglacial period facilitated population growth and range expansion leading to allopatric speciation. Here, we analyzed 40 genomes of four species of ibex and found that Himalayan ibex in the Pamir Mountains evolved independently after splitting from its main range about 0.1 mya following the Pleistocene species pump concept. Demographic trajectories showed Himalayan ibex experienced two historic bottlenecks, one each c. 0.8–0.5 mya and c. 50–30 kya, with an intermediate large population expansion c. 0.2–0.16 mya coinciding with Mid-Pleistocene Transitions. We substantiate with multi-dimensional evidence that Himalayan ibex is an evolutionary distinct phylogenetic species of Siberian ibex which need to be prioritized as Capra himalayensis for taxonomic revision and conservation planning at a regional and global scale.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Population Dynamics of Wild Goats)
►▼
Show Figures
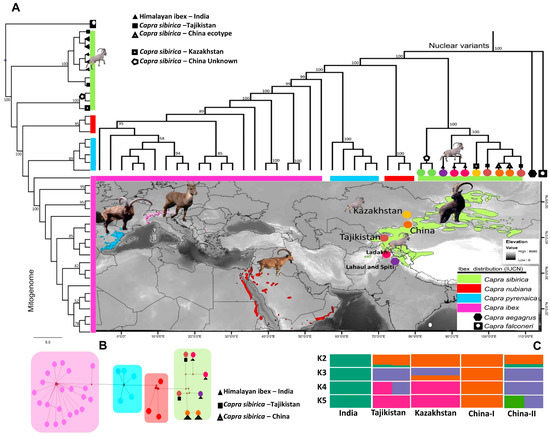
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
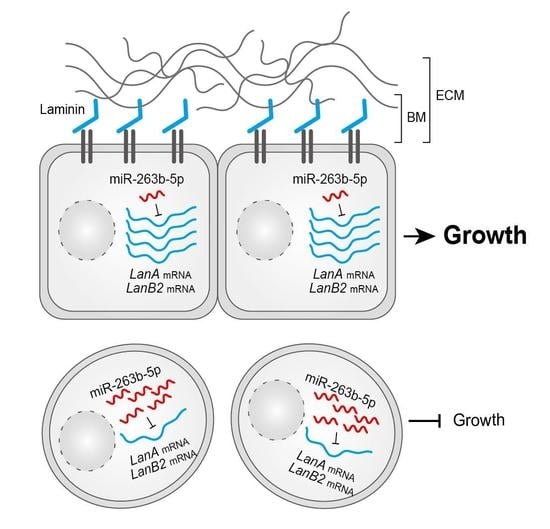
MicroRNA miR-263b-5p Regulates Developmental Growth and Cell Association by Suppressing Laminin A in Drosophila
by
, , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1096; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081096 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
Basement membranes (BMs) play important roles under various physiological conditions in animals, including ecdysozoans. During development, BMs undergo alterations through diverse intrinsic and extrinsic regulatory mechanisms; however, the full complement of pathways controlling these changes remain unclear. Here, we found that fat body-overexpression
[...] Read more.
Basement membranes (BMs) play important roles under various physiological conditions in animals, including ecdysozoans. During development, BMs undergo alterations through diverse intrinsic and extrinsic regulatory mechanisms; however, the full complement of pathways controlling these changes remain unclear. Here, we found that fat body-overexpression of Drosophila miR-263b, which is highly expressed during the larval-to-pupal transition, resulted in a decrease in the overall size of the larval fat body, and ultimately, in a severe growth defect accompanied by a reduction in cell proliferation and cell size. Interestingly, we further observed that a large proportion of the larval fat body cells were prematurely disassociated from each other. Moreover, we present evidence that miR-263b-5p suppresses the main component of BMs, Laminin A (LanA). Through experiments using RNA interference (RNAi) of LanA, we found that its depletion phenocopied the effects in miR-263b-overexpressing flies. Overall, our findings suggest a potential role for miR-263b in developmental growth and cell association by suppressing LanA expression in the Drosophila fat body.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Developmental Biology)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Lysine-Specific Demethylase 4D Is Critical for the Regulation of the Cell Cycle and Antioxidant Capacity in Goat Fibroblast Cells
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1095; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081095 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
Oxidative damage to skin fibroblast cells is a causative factor in many skin diseases. Previous studies have reported that lysine-specific demethylase 4D (Kdm4d) is involved in DNA replication, but its role on antioxidant capacity remains unclear. In the present study, we used goat
[...] Read more.
Oxidative damage to skin fibroblast cells is a causative factor in many skin diseases. Previous studies have reported that lysine-specific demethylase 4D (Kdm4d) is involved in DNA replication, but its role on antioxidant capacity remains unclear. In the present study, we used goat fibroblast cells (GFCs) as the research model and identified 504 up-regulated and 1013 down-regulated genes following the knockdown of Kdm4d, respectively. The down-regulated genes of this enzyme were found to be enriched in the cell cycle, DNA replication, mitotic processes, and the oxidative phosphorylation pathway, as previously revealed from gene ontology (GO), Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG), and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA), suggesting vital roles of the Kdm4d enzyme in the cell cycle and in antioxidant regulation. To this end, we found the cell proliferation rate was significantly decreased after the knockdown of Kdm4d. Moreover, both the mRNA and protein expression levels of superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2), one of the major antioxidant enzymes, was decreased, while the reactive oxygen species (ROS) level was significantly increased in Kdm4d knocked-down cells. In addition, the expression of γH2A histone family member X (γH2AX) increased significantly, indicating the presence of DNA double-strand breaks after the knockdown of the Kdm4d enzyme. In conclusion, the knockdown of Kdm4d inhibited DNA replication and the cell cycle, repressed the expression of SOD2, and increased the generation of ROS, which led to the production of DNA damage in GFCs. Our data will be helpful for understanding the mechanism underlying antioxidant capacity regulation in fibroblast cells.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cell Biology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
In Silico Virome Analysis of Chinese Narcissus Transcriptomes Reveals Diverse Virus Species and Genetic Diversity at Different Flower Development Stages
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1094; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081094 - 05 Aug 2023
Abstract
Viromes of Chinese narcissus flowers were explored using transcriptome data from 20 samples collected at different flower development stages. Quality controlled raw data underwent de novo assembly, resulting in 5893 viral contigs that matched the seven virus species. The most abundant viruses were
[...] Read more.
Viromes of Chinese narcissus flowers were explored using transcriptome data from 20 samples collected at different flower development stages. Quality controlled raw data underwent de novo assembly, resulting in 5893 viral contigs that matched the seven virus species. The most abundant viruses were narcissus common latent virus (NCLV), narcissus yellow stripe virus (NYSV), and narcissus mottling-associated virus (NMaV). As flower development stages advanced, white tepal plants showed an increase in the proportion of viral reads, while the variation in viral proportion among yellow tepal plants was relatively small. Narcissus degeneration virus (NDV) dominated the white tepal samples, whereas NDV and NYSV prevailed in the yellow tepal samples. Potyviruses, particularly NDV, are the primary infectious viruses. De novo assembly generated viral contigs for five viruses, yielding complete genomes for NCLV, NDV, narcissus late season yellow virus (NLSYV), and NYSV. Phylogenetic analysis revealed genetic diversity, with distinct NCLV, NMaV, NDV, NLSYV, and NYSV groups. This study provides valuable insights into the viromes and genetic diversity of viruses in Chinese narcissus flowers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Recent Advances in Agricultural-Associated Viruses)
►▼
Show Figures
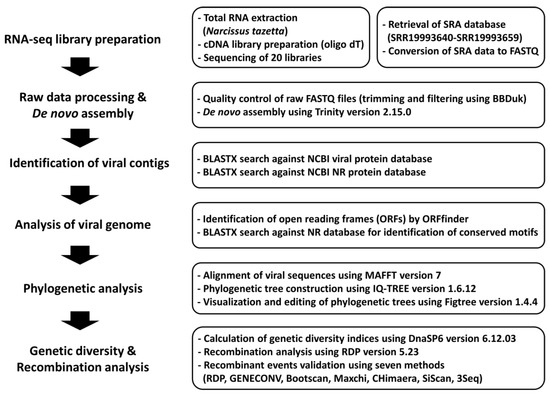
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Combined Use of a Bacterial Consortium and Early-Colonizing Plants as a Treatment for Soil Recovery after Fire: A Model Based on Los Guájares (Granada, Spain) Wildfire
by
, , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1093; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081093 - 05 Aug 2023
Abstract
During 2022, intense heat waves, together with particularly extreme dry conditions, created a propitious scenario for wildfires, resulting in the area of vegetation consumed in Europe doubling. Mediterranean countries have been particularly affected, reaching 293,155 hectares in Spain, the worst data in the
[...] Read more.
During 2022, intense heat waves, together with particularly extreme dry conditions, created a propitious scenario for wildfires, resulting in the area of vegetation consumed in Europe doubling. Mediterranean countries have been particularly affected, reaching 293,155 hectares in Spain, the worst data in the last 15 years. The effects on the vegetation and the soil are devastating, so knowing the recovery factors is essential for after-fire management. Resilient microorganisms play a fundamental role in rapid nutrient recycling, soil structure, and plant colonization in fire-affected soils. In this present work, we have studied emergent microbial communities in the case of the Los Guájares (Granada, Spain) fire, one of the most extensive of the year, to evaluate their role in the recovery of soil and vegetation cover. We aim to discern which are the main actors in order to formulate a new treatment that helps in the ecosystem recovery. Thus, we have found the relevant loss in phosphorous and potassium solubilizers, as well as siderophores or biofilm producers. Here, we decided to use the strains Pseudomonas koreensis AC, Peribacillus frigoritolerans CB, Pseudomonas fluorescens DC, Paenibacillus lautus C, Bacillus toyonensis CD, and Paenarthrobacter nitroguajacolicus AI as a consortium, as they showed most of the capacities required in a regenerative treatment. On the other hand, the microcosm test showed an enhanced pattern of germination of the emerging model plant, Bituminaria bituminosa, as well as a more aggregated structure for soil. This new approach can create a relevant approach in order to recover fire-affected soils in the future.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents LPS-Induced Depression-like Behavior through the Suppression of NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis and the Improvement of Mitochondrial Function in the Hippocampus of Mice
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1092; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081092 - 05 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) has been implicated to have antidepressive effects. We sought to investigate the prevention effects of H2S donor NaHS on depression-like behavior induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in mice and its potential mechanisms. Sucrose preference, force swimming, open
[...] Read more.
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) has been implicated to have antidepressive effects. We sought to investigate the prevention effects of H2S donor NaHS on depression-like behavior induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in mice and its potential mechanisms. Sucrose preference, force swimming, open field, and elevate zero maze were used to evaluate depression-like behavior. NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation and mitochondrial function in the hippocampus were determined. It was found that depression-like behavior induced by LPS was prevented by NaHS pretreatment. LPS caused NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in the hippocampus as evidenced by increased phosphorylated-p65 levels and increased NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1, and mature IL-1β levels in the hippocampus, which were also blocked by NaHS. LPS increased GSDMD-N levels and TUNEL-positive cells in the hippocampus, which was prevented by NaHS. Abnormal mitochondrial morphology in the hippocampus was found in LPS-treated mice. Mitochondrial membrane potential and ATP production were reduced, and ROS production was increased in the hippocampus of LPS-treated mice. NaHS pretreatment improved impaired mitochondrial morphology and increased membrane potential and ATP production and reduced ROS production in the hippocampus of LPS-treated mice. Our data indicate that H2S prevents LPS-induced depression-like behaviors by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis and improving mitochondrial function in the hippocampus.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Towards an Understanding of Microglia and Border-Associated Macrophages
by
and
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1091; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081091 - 05 Aug 2023
Abstract
The central nervous system (CNS) plays a crucial role in regulating bodily functions by sensing and integrating environmental cues and maintaining proper physiological conditions. Recent research has revealed that CNS functions are closely coordinated with the immune system. As even minor disturbances of
[...] Read more.
The central nervous system (CNS) plays a crucial role in regulating bodily functions by sensing and integrating environmental cues and maintaining proper physiological conditions. Recent research has revealed that CNS functions are closely coordinated with the immune system. As even minor disturbances of the immune system in the CNS can lead to various dysfunctions, diseases, or even death, it is highly specialized and segregated from that in peripheral regions. Microglia in the parenchyma and macrophages at the interface between the CNS and peripheral regions are essential immune cells in the CNS that monitor environmental changes. Recent omics analyses have revealed that these cells exhibit highly heterogeneous populations. In this review, we summarize the functions and diversity of microglia in the brain parenchyma and those of macrophages in the border regions, such as the meninges, perivascular spaces, and choroid plexus.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Insights into the Roles of Glia in Physiology and Pathophysiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Adaptability and Germination Characteristics of Volunteer Wheat in China’s Main Wheat-Producing Areas
by
, , , , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1090; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081090 - 04 Aug 2023
Abstract
Volunteer wheat commonly occurs and spreads rapidly in the main wheat-producing areas of China, seriously impacting cultivated wheat production. Limited information is currently available regarding the adaptability and germination traits of volunteer wheat. Therefore, this study’s aim was to evaluate the effects of
[...] Read more.
Volunteer wheat commonly occurs and spreads rapidly in the main wheat-producing areas of China, seriously impacting cultivated wheat production. Limited information is currently available regarding the adaptability and germination traits of volunteer wheat. Therefore, this study’s aim was to evaluate the effects of environmental conditions on the germination and emergence of volunteer wheat seeds through laboratory experiments. The results showed that the germination percentages and viability of volunteer wheat were significantly higher than those of cultivated wheat at a low temperature of 5 °C, and they were lower than those of cultivated wheat at high temperatures of above 30 °C. Compared to cultivated wheat, volunteer wheat was able to tolerate higher salinity and lower osmotic potential, especially long-dormancy volunteer wheat. The secondary germination ability of volunteer wheat was higher than that of cultivated wheat after water immersion. Furthermore, volunteer wheat could not emerge normally when the seeding depth was greater than 8 cm, and the emergence ability of the volunteer wheat was weaker than that of the cultivated wheats when the seeding depth was 4–8 cm, which indicates that the deep tillage of cultivated land could effectively prevent the spread of volunteer wheat. This study revealed differences in the germination characteristics of volunteer wheat and cultivated wheat under the influence of different environmental factors, which provides a basis for future studies concerning the control of volunteer wheat.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Advances in Weed Biology, Ecology and Management)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessStudy Protocol
Sports-Related Concussion Assessment: A New Physiological, Biomechanical, and Cognitive Methodology Incorporating a Randomized Controlled Trial Study Protocol
by
, , , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1089; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081089 - 04 Aug 2023
Abstract
Background: Taking part in moderate-to-vigorous exercise in contact sports on a regular basis may be linked to an increase in cerebrovascular injury and head trauma. Validated objective measures are lacking in the initial post-event diagnosis of head injury. The exercise style, duration, and
[...] Read more.
Background: Taking part in moderate-to-vigorous exercise in contact sports on a regular basis may be linked to an increase in cerebrovascular injury and head trauma. Validated objective measures are lacking in the initial post-event diagnosis of head injury. The exercise style, duration, and intensity may also confound diagnostic indicators. As a result, we propose that the new Interdisciplinary Group in Movement & Performance from Acute & Chronic Head Trauma (IMPACT) analyze a variety of functional (biomechanical and motor control) tests as well as related biochemistry to see how they are affected by contact in sports and head injury. The study’s goal will be to look into the performance and physiological changes in rugby players after a game for head trauma and injury. Methods: This one-of-a-kind study will use a randomized controlled trial (RCT) utilizing a sport participation group and a non-participation control group. Forty male rugby 7 s players will be recruited for the study and allocated randomly to the experimental groups. The intervention group will participate in three straight rugby matches during a local 7 s rugby event. At the pre-match baseline, demographic and anthropometric data will be collected. This will be followed by the pre-match baseline collection of biochemical, biomechanical, and cognitive-motor task data. After three consecutive matches, the same measures will be taken. During each match, a notational analysis will be undertaken to obtain contact information. All measurements will be taken again 24, 48, and 72 h after the third match. Discussion: When the number of games increases owing to weariness and/or stressful circumstances, we expect a decline in body movement, coordination, and cognitive-motor tasks. Changes in blood biochemistry are expected to correspond to changes in biomechanics and cognitive-motor processes. This research proposal will generate considerable, ecologically valid data on the occurrence of head trauma events under game conditions, as well as the influence of these events on the biological systems of the performers. This will lead to a greater understanding of how sports participants react to exercise-induced injuries. This study’s scope will have far-reaching ramifications for doctors, coaches, managers, scientists, and sports regulatory bodies concerned with the health and well-being of athletic populations at all levels of competition, including all genders and ages.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effects of Physical Exercise on Human Physiology and Pathology)
►▼
Show Figures
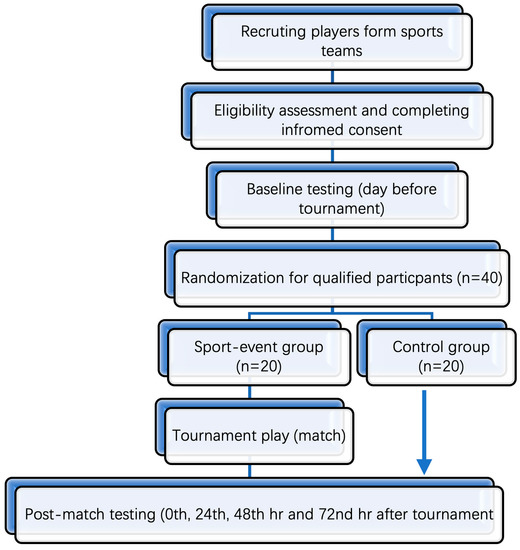
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Aging Increases Enterocyte Damage during a 3-Hour Exposure to Very Hot and Dry Heat: A Preliminary Study
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1088; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081088 - 04 Aug 2023
Abstract
Profound heat stress can damage the gastrointestinal barrier, leading to microbial translocation from the gut and subsequent systemic inflammation. Despite the greater vulnerability of older people to heat wave-related morbidity and mortality, it is unknown if age modulates gastrointestinal barrier damage and inflammation
[...] Read more.
Profound heat stress can damage the gastrointestinal barrier, leading to microbial translocation from the gut and subsequent systemic inflammation. Despite the greater vulnerability of older people to heat wave-related morbidity and mortality, it is unknown if age modulates gastrointestinal barrier damage and inflammation during heat stress. Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine if aging impacted enterocyte damage and systemic inflammatory responses to a 3-h exposure to very hot and dry (47 °C, 15% humidity) heat with accompanying activities of daily living (intermittent activity at 3 METS). Data from 16 young (age 21 to 39 years) and 16 older (age 65 to 76 years) humans were used to address this aim. In each group, log-transformed plasma concentrations of intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABPlog), interleukin-8 (IL-8log), and tissue factor (TFlog) were assessed as indices of enterocyte damage, systemic inflammation, and blood coagulation, respectively, before and after the 3-h heat exposure. In the younger cohort, I-FABPlog concentration did not increase from pre to post heat exposure (p = 0.264, d = 0.20), although it was elevated in the older group (p = 0.014, d = 0.67). The magnitude of the increase in I-FABPlog was greater in the older participants (p = 0.084, d = 0.55). Across all participants, there was no correlation between the change in core temperature and the change in IFABPlog. There was no change in IL-8log in the younger group (p = 0.193, d = 0.23) following heat exposure, but we observed a decrease in IL-8log in the older group (p = 0.047, d = 0.48). TFlog decreased in the younger group (p = 0.071, d = 0.41), but did not change in the older group (p = 0.193, d = 0.15). Our data indicate that I-FABPlog concentration (an index of enterocyte damage) is increased in older humans during a 3-h extreme heat exposure. Future studies should determine whether this marker reflects increased gastrointestinal barrier permeability in older individuals during heat exposure.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Effects of Environmental Factors on Human Health and Performance)
►▼
Show Figures
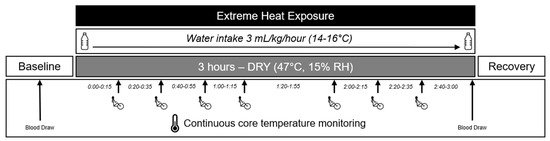
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Biomarkers of Type IV Collagen Turnover Reflect Disease Activity in Patients with Early-Stage Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver (NAFL)
by
, , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1087; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081087 - 04 Aug 2023
Abstract
Background: Identification of progressive liver disease necessitates the finding of novel non-invasive methods to identify and monitor patients in need of early intervention. Investigating patients with early-liver injury may help identify unique biomarkers. Early-liver injury is characterized by remodeling of the hepatocyte basement
[...] Read more.
Background: Identification of progressive liver disease necessitates the finding of novel non-invasive methods to identify and monitor patients in need of early intervention. Investigating patients with early-liver injury may help identify unique biomarkers. Early-liver injury is characterized by remodeling of the hepatocyte basement membrane (BM) of the extracellular matrix. Thus, we quantified biomarkers targeting two distinct neo-epitopes of the major BM collagen, type IV collagen (PRO-C4 and C4M), in patients spanning the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) spectrum. Methods: We evaluated PRO-C4 and C4M in a cross-sectional study with 97 patients with NAFLD confirmed on histology. Serological levels of PRO-C4 and C4M were quantified using validated competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA). Using the fatty liver inhibition of progression (FLIP) algorithm, we stratified patients into two groups: non-alcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Biomarker levels were investigated in the two groups in patients stratified by the NAFLD activity score (NAS). In both groups, biomarker measurements were analyzed in relation to histological scorings of steatosis, inflammation, ballooning, and fibrosis. Results: Patients had a body mass index (BMI) of 30.9 ± 5.6 kg/m2, age of 53 ± 13 years and a NAS range of 1–8. Upon stratification by FLIP, the NASH patients had higher platelets, ALT, and AST levels than the NAFL group. Both PRO-C4 (p = 0.0125) and C4M (p = 0.003) increased with increasing NAS solely within the NAFL group; however, a large variability was present in the NASH group. Furthermore, both markers were significantly associated with lobular inflammation (p = 0.020 and p = 0.048) and steatosis (p = 0.004 and p = 0.015) in patients with NAFL. Conclusions: This study found that type IV collagen turnover increased with the increase in NAS in patients with NAFL; however, this was not the case in patients with NASH. These findings support the assessments of the BM turnover using biomarkers in patients with early-disease development. These biomarkers may be used to track specific processes involved in the early pathobiology of NAFL.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Chronic Liver Disease: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Practice)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Motility Subpopulations with Distinct Motility Characteristics Using Swim-Up-Selected Sperm Cells from Norwegian Red Bulls: Effects of Freezing–Thawing and Between-Bull Variation
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1086; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081086 - 03 Aug 2023
Abstract
Discrete subpopulations of motile sperm cells have been found for several species and are implicated to be important for sperm functionality. The aim of this present study was to examine the motile subpopulations in swim-up-selected bull spermatozoa and the relationship between subpopulations in
[...] Read more.
Discrete subpopulations of motile sperm cells have been found for several species and are implicated to be important for sperm functionality. The aim of this present study was to examine the motile subpopulations in swim-up-selected bull spermatozoa and the relationship between subpopulations in fresh and frozen–thawed sperm cells. In experiment 1, swim-up (SWUP)-selected and non-selected (control) sperm cells were analyzed using a Computer-Assisted Sperm Analyzer (CASA). In experiment 2, the semen from nine bulls was cryopreserved and analyzed using CASA both before and after freezing and after incubation at physiological temperatures. The SWUP population had a higher proportion of total motility, progressivity, and velocity compared to the control (p < 0.05). Likewise, both incubation over time and cryopreservation affected motility and motility parameters (p < 0.05). The population of rapid progressive (RapidP) sperm cells dominated the SWUP fraction and was higher than in the control samples (p < 0.05). Furthermore, RapidP was also the main part of fresh semen, but decreased significantly over time during incubation and due to cryopreservation. In conclusion, RapidP was the main population in SWUP-selected spermatozoa and seems to be an important subpopulation contributing to the differences between treatments and in response to the freezing of sperm cells.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Reproductive Biology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Preparation of Fibrinogen-Depleted Human Platelet Lysate to Support Heparin-Free Expansion of Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
by
, , , , , , and
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1085; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081085 - 03 Aug 2023
Abstract
Human platelet lysate (hPL) has high levels of fibrinogen and coagulation factors, which can lead to gel and precipitate formation during storage and cell culture. Heparin derived from animals is commonly added to minimize these risks, but cannot completely eliminate them. Thus, this
[...] Read more.
Human platelet lysate (hPL) has high levels of fibrinogen and coagulation factors, which can lead to gel and precipitate formation during storage and cell culture. Heparin derived from animals is commonly added to minimize these risks, but cannot completely eliminate them. Thus, this study proposes an alternative method to prepare fibrinogen-depleted hPL (Fd-hPL) that supports heparin-free expansion of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). hPL was added to heparin to prepare heparin-hPL (H-hPL), whilst Fd-hPL was prepared by adding calcium salt to hPL to remove the fibrin clot. The concentrations of calcium, fibrinogen, and growth factors in H-hPL and Fd-hPL were compared. The effects of H-hPL and Fd-hPL on umbilical cord-derived MSCs (UC-MSCs) were assessed. The results showed that Fd-hPL possessed a significantly higher calcium concentration and a lower fibrinogen level than H-hPL. The concentrations of BDNF, TGF-β1, and PDGF-BB showed no significant difference between H-hPL and Fd-hPL, but Fd-hPL had a lower VEGF concentration. Fd-hPL retained the characteristics of UC-MSCs, as it did not affect the cell viability, proliferation, multilineage differentiation potential, or surface marker expression. In conclusion, Fd-hPL effectively supported the in vitro expansion of MSCs without compromising their characteristics, positioning it as a potential substitute for FBS in MSC culture.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mesenchymal Stem Cells: What We Have Learned and How to Manage Them)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Relevance of Time in Biological Scaling
Biology 2023, 12(8), 1084; https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12081084 - 03 Aug 2023
Abstract
Various phenotypic traits relate to the size of a living system in regular but often disproportionate (allometric) ways. These “biological scaling” relationships have been studied by biologists for over a century, but their causes remain hotly debated. Here, I focus on the patterns
[...] Read more.
Various phenotypic traits relate to the size of a living system in regular but often disproportionate (allometric) ways. These “biological scaling” relationships have been studied by biologists for over a century, but their causes remain hotly debated. Here, I focus on the patterns and possible causes of the body-mass scaling of the rates/durations of various biological processes and life-history events, i.e., the “pace of life”. Many biologists have regarded the rate of metabolism or energy use as the master driver of the “pace of life” and its scaling with body size. Although this “energy perspective” has provided valuable insight, here I argue that a “time perspective” may be equally or even more important. I evaluate various major ways that time may be relevant in biological scaling, including as (1) an independent “fourth dimension” in biological dimensional analyses, (2) a universal “biological clock” that synchronizes various biological rates/durations, (3) a scaling method that uses various biological time periods (allochrony) as scaling metrics, rather than various measures of physical size (allometry), as traditionally performed, (4) an ultimate body-size-related constraint on the rates/timing of biological processes/events that is set by the inevitability of death, and (5) a geological “deep time” approach for viewing the evolution of biological scaling patterns. Although previously proposed universal four-dimensional space-time and “biological clock” views of biological scaling are problematic, novel approaches using allochronic analyses and time perspectives based on size-related rates of individual mortality and species origination/extinction may provide new valuable insights.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Ecology)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Biology Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biology, Biomedicines, Cancers, Current Oncology, Onco
Targeting Signaling Networks for Cancer Therapy
Topic Editors: Renato Bassan, Jose-Maria Ribera, Linlin GuoDeadline: 5 September 2023
Topic in
Cancers, Biology, Current Oncology, IJMS, JCM
Advances in Molecular and Cellular Studies in Oral Diseases
Topic Editors: Bing Liu, Ming ZhongDeadline: 20 September 2023
Topic in
Biology, Cells, IJMS, Organoids
Pluripotent Stem Cells
Topic Editors: Dongsheng Guo, Xianming Wang, Yuelin Zhang, Linpeng Li, Kepin WangDeadline: 1 October 2023
Topic in
IJERPH, JCM, Biology, Diagnostics, Dentistry Journal
Diagnosis of Craniofacial Changes: Conventional Approaches and Novel Methodologies
Topic Editors: Nikolaos Gkantidis, Carlalberta VernaDeadline: 20 October 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Biology
Antibiotic Resistance: Linking Phenotypes and Mechanisms
Guest Editor: Fernando BaqueroDeadline: 15 August 2023
Special Issue in
Biology
Plant Functional Genomics in the Era of Omics Approaches
Guest Editors: Mariateresa Volpicella, Cinzia MontemurroDeadline: 31 August 2023
Special Issue in
Biology
Metabolism of Hematopoietic Stem Cells during Development and Aging
Guest Editor: Tasleem ArifDeadline: 15 September 2023
Special Issue in
Biology
Chemical Contaminants and Environmental Health
Guest Editors: Zulin Zhang, Yongzhen Ding, Ping Li, Song Cui, Xuebin QiDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Biology
Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Cereals
Collection Editor: Dorothea Bartels
Topical Collection in
Biology
Crop Improvement Now and Beyond
Collection Editors: Pierre Devaux, Pierre Sourdille
Topical Collection in
Biology
Gap Junctions and Connexins in Physiology, Pharmacology and Disease
Collection Editors: Yi Zhu, Sebastian Curti, Xinbo Li
Topical Collection in
Biology
Molecular Mechanisms of Aging
Collection Editors: Serena Dato, Giuseppina Rose, Paolina Crocco










.jpg)








