-
 Sol–Gel Silica Coatings for Corrosion Protection of Aluminum Parts Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting (SLM) Technology
Sol–Gel Silica Coatings for Corrosion Protection of Aluminum Parts Manufactured by Selective Laser Melting (SLM) Technology -
 Comparative Analysis of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Utilizing Spirulina-Derived Pigment as a Bio-Based Colorant for Wood Impregnator
Comparative Analysis of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Utilizing Spirulina-Derived Pigment as a Bio-Based Colorant for Wood Impregnator -
 Role of the Alkylation Patterning in the Performance of OTFTs: The Case of Thiophene-Functionalized Triindoles
Role of the Alkylation Patterning in the Performance of OTFTs: The Case of Thiophene-Functionalized Triindoles
Journal Description
Coatings
Coatings
is a peer-reviewed journal of coatings and surface engineering published monthly online by MDPI. The Korean Tribology Society (KTS) is affiliated with Coatings and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), Inspec, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Materials Science, Coatings & Films) / CiteScore - Q2 (Surfaces and Interfaces)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 12.4 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 15 topical sections.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Coatings.
Impact Factor:
3.4 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.4 (2022)
Latest Articles
Smart Asphalt Mixtures: A Bibliometric Analysis of the Research Trends
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1396; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081396 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
A smart asphalt mixture holds new capabilities different from the original ones or can react to a stimulus. These capabilities can be categorized based on smartness or function: smartness, mechanical, electrical, optical, energy harvesting, electromagnetic wave/radiation shielding/absorbing, and water related. The most important
[...] Read more.
A smart asphalt mixture holds new capabilities different from the original ones or can react to a stimulus. These capabilities can be categorized based on smartness or function: smartness, mechanical, electrical, optical, energy harvesting, electromagnetic wave/radiation shielding/absorbing, and water related. The most important capabilities applied to asphalt mixtures are the photocatalytic, self-cleaning, self-healing, superhydrophobic, thermochromic, deicing/anti-icing, and latent heat thermal energy storage abilities. This research deals with a bibliometric review of the peer-reviewed journal articles published on the Scopus database, with the strings of terms related to these capabilities and asphalt or bitum in their titles, abstracts, and keywords. The review analysis highlighted the increasing number of accumulated publications, confirming the relevance of this research topic in recent years. The capability most often referred to was self-healing. The study showed that China was the most productive country. Research articles were mostly published in the journal Construction and Building Materials. Several techniques and methods are being developed regarding smart asphalt mixtures; for that reason, this research work aims to evaluate the literature under a bibliometric analysis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Surface Characterization, Deposition and Modification)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Development of Laser Cavitation Peening Using a Normal-Oscillation Nd:YAG Laser
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1395; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081395 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The impact induced by cavitation bubble collapse can be utilized for mechanical surface treatment to improve fatigue properties of metals including additive manufactured metallic materials. A peening method using cavitation impact induced by a pulsed laser is called “laser cavitation peening (LCP)”. Normally,
[...] Read more.
The impact induced by cavitation bubble collapse can be utilized for mechanical surface treatment to improve fatigue properties of metals including additive manufactured metallic materials. A peening method using cavitation impact induced by a pulsed laser is called “laser cavitation peening (LCP)”. Normally, a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser, whose pulse width is a few nanoseconds, is used for LCP, which improves the fatigue strength. The problem with LCP is that the processing time is too slow. If a laser pulse whose pulse width is a few hundred microseconds can be utilized for LCP, the repetition frequency can be increased drastically using other types of laser systems such as a fiber laser. In the present paper, in order to reveal the possibility of LCP using a pulsed laser width of a few hundred microseconds, the use of LCP with a normal-oscillation Nd:YAG laser (pulse width ≈ 200 μs) was investigated. It is demonstrated that LCP with the normal-oscillation Nd:YAG laser produced curvature in an aluminum alloy plate. The shock pressure wave and impulsive vibration of the target surface at the first collapse of laser cavitation (LC), which was induced by the normal-oscillation Nd:YAG laser, was 3–4 times larger than those of laser ablation (LA).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Laser Surface Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
UV-Curable Fluorocarbon Polyurethane Coatings for Marble Kitchen Countertops
by
and
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1394; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081394 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Marble kitchen countertops and other natural stone surfaces are often stained by various food ingredients and contaminants during daily use and require frequent cleaning, which is time-consuming and leads to the wasting of water. If the surface is coated with a hydrophobic and
[...] Read more.
Marble kitchen countertops and other natural stone surfaces are often stained by various food ingredients and contaminants during daily use and require frequent cleaning, which is time-consuming and leads to the wasting of water. If the surface is coated with a hydrophobic and oleophobic coating, food ingredient contamination becomes easier to wipe clean. Therefore, a UV-curable monomer with fluorocarbon branched chains was synthesized and added to UV-curable coatings in different ratios. The preferred formulation that meets the basic performance requirements of UV-curable coatings, and has the best hydrophobic and oleophobic properties, was designed and selected. The formulation was upgraded by adding a hydrofluoric ether (HFE) solvent. These upgraded formulations were tested for hydrophobicity and oleophobicity under various conditions. The addition of an HFE solvent improves the initial water and cetane contact angles of the paint film, as well as the water and cetane contact angles under various conditions. Moreover, the upgraded formulations have better stain resistance. The degree of hydrophobicity and oleophobicity improvement is positively correlated with the addition of an HFE solvent. The UV-curable fluorocarbon polyurethane coating has good adhesion on a marble surface that has been polished and primed. Due to the presence of TEOH-6 instead of PFOA, the low content of fluorocarbon functional groups effectively located on the film surface makes the coating quite stable and safe.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Role of Friction Stir Processing Parameters and Hybrid ZrC/WC Reinforcement Particles in Improving the Surface Composite Dissimilar Matrix’s Dynamic Behavior and Microstructure Refinement
by
, , , , and
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1393; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081393 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study examined the impact of hybrid reinforcement particles, specifically zirconium carbide (ZrC) and tungsten carbide (WC), as well as the parameters of friction stir processing (FSP), on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and dynamic behavior of aluminum alloys. The hybrid particles were integrated
[...] Read more.
This study examined the impact of hybrid reinforcement particles, specifically zirconium carbide (ZrC) and tungsten carbide (WC), as well as the parameters of friction stir processing (FSP), on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and dynamic behavior of aluminum alloys. The hybrid particles were integrated into the aluminum alloy using friction stir processing (FSP). The fabricated metal matrix composites (MMCs) were characterized using optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA). The results showed that the FSP parameters and reinforcement particles played an important role in improving the grain refinement of the MMCs. This study’s results suggest that the FSP samples’ UTS can be maximized using a tool rotation speed of 600 rpm and a traverse speed of 30 mm/min. The grain refinement in the composite surface was attributed to the dynamic recrystallization during the friction stir processing (FSP) process. The reinforcement particles also acted as grain growth restrictors, further refining the grain size. This resulted in a 34% increase in ultimate tensile strength compared to AA2024 alloys and a 12% increase compared to AA7075 alloys. The composite surface also exhibited enhanced dynamic properties, with an increase in impact energy of 26%. The free vibration test showed that the hybrid reinforcement particles significantly improved the strength and damping capacity of the aluminum alloys, resulting in a high resonant frequency. This is important for applications such as vibration damping and noise reduction.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Surface Modification, Properties, Performance and Analysis Technology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Carbon Nanocoil-Based Photothermal Conversion Carrier for Microbubble Transport
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1392; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081392 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Carbon nanocoil (CNC), a kind of quasi-one-dimensional carbon nanomaterial with a unique micro-scale helical structure, has wide application prospects in biological and environmental governance fields, due to its excellent photothermal conversion characteristics. We combine a carbon nanocoil as the laser irradiation carrier (i.e.,
[...] Read more.
Carbon nanocoil (CNC), a kind of quasi-one-dimensional carbon nanomaterial with a unique micro-scale helical structure, has wide application prospects in biological and environmental governance fields, due to its excellent photothermal conversion characteristics. We combine a carbon nanocoil as the laser irradiation carrier (i.e., the substance for absorbing light energy and converting light energy into heat to allow the creation of microbubbles) and a light-induced method to realize the radial short-distance transport of microbubbles. The results confirm that controlling the size of the microbubbles by laser power enables the radial transport of multiple microbubbles in a row. Light-induced CNC allows the creation of microbubbles at the start of the transport and the elimination of the microbubbles at the end of the transport, and the distance of transport between the laser irradiation site on the CNC and the location of the bubbles disappearing ranges from 10 µm to 30 µm. The circulation process of creating, transporting, and eliminating bubbles is expected to become a promising technology for soil and groundwater remediation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Enhanced Thin-Film Application on Sensors)
►▼
Show Figures
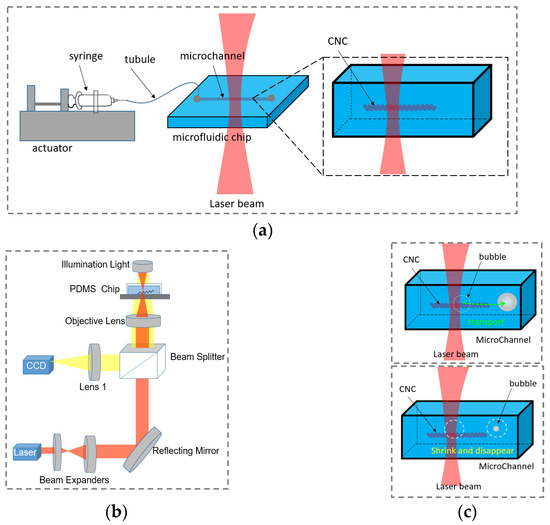
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Optimized Dip Coating Approach for Metallic, Dielectric, and Semiconducting Nanomaterial-Based Optical Thin Film Fabrication
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1391; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081391 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The field of optical thin films has garnered significant attention due to their potential applications in visible light communication, optical sensing, and imaging. Among the various fabrication methods available, conventional layer-by-layer (LBL) dip coating is less sophisticated and more economical. Nevertheless, this approach
[...] Read more.
The field of optical thin films has garnered significant attention due to their potential applications in visible light communication, optical sensing, and imaging. Among the various fabrication methods available, conventional layer-by-layer (LBL) dip coating is less sophisticated and more economical. Nevertheless, this approach frequently encounters deficiencies in the precise control of the growth of thin films. This work aimed at properly comprehending the growth conditions associated with the LBL dip coating process and optimizing the conditions to obtain the best thin film growth for different materials: metallic (Ag), semiconducting (ZnO), and insulating (SiO2). The optimization of the conditions for surface functionalization with 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) together with other parameters like dipping time, drying time, the number of dipping–drying cycles, and the timing of the intermediate APTES layers led to the controlled growth of thin films. Atomic force microscopy and scanning electron microscopy revealed even deposition in the case of ZnO and SiO2 from the very beginning, while with Ag NPs, the growth of the thin film was observed to be uneven and gradually became smooth as the number of layers increased, and a smooth layer could be observed after over 100 layers of dipping.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Functional Surfaces and Interfaces)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Insights into Interfacial Features of Metal/Eco-Composites Designed for Energy Storage
by
, , , , and
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1390; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081390 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The development of innovative materials with improved properties is required for the field of energy storage. This article proves that it is possible to utilize bio-derived fillers to tune the performance of biodegradable polymers. For this scope, eco-composites were attained by loading several
[...] Read more.
The development of innovative materials with improved properties is required for the field of energy storage. This article proves that it is possible to utilize bio-derived fillers to tune the performance of biodegradable polymers. For this scope, eco-composites were attained by loading several amounts of walnut leaf powder (WLP) in hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC). Basic testing was conducted to emphasize the sample’s suitability for the pursued application. The rheological behavior was altered with the addition of WLP at low shear rates, which became more pseudoplastic, resulting in composite films with higher thickness uniformity. Wettability characteristics were used to analyze the macro-level adhesion of the platinum-containing samples, and the results showed that the presence of WLP led to the augmentation of interfacial compatibilization of the composite with the metal layer. The electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy scans showed the proper distribution of the WLP in the matrix. Local adhesion data derived from DFL-height curves further showed that the inclusion of WLP improves the adhesion capabilities at the nanoscale. The dielectric spectroscopy tests proved that the used biofiller leads to an enhancement in the permittivity of the composite with respect to the neat HEC. By accounting for all results, the generated eco-composites are suggested as alternative dielectrics for usage in the energy storage domain.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Metallic Thin Films and Current Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
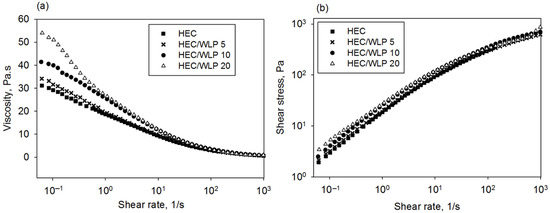
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Thin Cationic Polymer Coatings against Foodborne Infections
by
, , , , , , , , , , , , and
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1389; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081389 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Biocidal coatings are known to minimize or terminate development of bacterial and fungicidal infections. In this paper, biocidal activity of seven cationic (co)polymers with amino groups—polyethyleneimine, polyallylamine, polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride/polyhexamethylene guanidine copolymer, diallyldimethylammonium chloride/SO2 copolymer, linear and hyperbranched epichlorohydrin/dimethylamine copolymers, polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride—were tested
[...] Read more.
Biocidal coatings are known to minimize or terminate development of bacterial and fungicidal infections. In this paper, biocidal activity of seven cationic (co)polymers with amino groups—polyethyleneimine, polyallylamine, polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride/polyhexamethylene guanidine copolymer, diallyldimethylammonium chloride/SO2 copolymer, linear and hyperbranched epichlorohydrin/dimethylamine copolymers, polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride—were tested toward Gram-positive and Gram-negative cells. The polymers showed a significant biocidal effect in both aqueous solution and after formation of polymer films on the hydrophilic glass plates. Polymer films were almost completely removed by water during 10 wash-off cycles, that finally resulted in the ultrathin monolayers with a thickness of several nanometers. A polyethyleneimine film showed the most resistance to water with a 50% loss after three wash-off cycles and 75% loss after six wash-off cycles. Binding and subsequent deactivation of pathogenic microorganisms occurs on the outer surface of cationic polymer films. It is expected that a gradual polymer wash-off will allow renewal of the outer film surface and thereby restore the biocidal properties of the polycationic coatings, including those with a nanoscale thickness.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Biofilms: Composition and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optical Trapping and Manipulation of Nanoparticles on Plasmonic Silicon-Nanostructured Array Coating on Silicon Film
by
, , , , , , , and
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1388; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081388 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
A silicon-nanostructured array coating on silicon film (SAS film) is designed based on the plasmonic optical tweezer and demonstrated for optical trapping and manipulation of nanospheres with negligible impact on the local thermal conditions. The electric field enhancement, optical force, and trapping potential
[...] Read more.
A silicon-nanostructured array coating on silicon film (SAS film) is designed based on the plasmonic optical tweezer and demonstrated for optical trapping and manipulation of nanospheres with negligible impact on the local thermal conditions. The electric field enhancement, optical force, and trapping potential of the SAS film are investigated by the finite element method. The trapping position is affected by the incident light wavelength, structure of the nanoarray, and refractive index of the nanospheres. The presence of four energy wells around the nanoarray suggests that it is possible to trap multiple nanoparticles. Moreover, the circularly polarized light, Gaussian beam, and silicon nanoarray facilitate the trapping of nanoparticles. This study showcases the potential of SAS film as optical tweezers to capture nanoparticles for the development of nanophotonic devices.
Full article
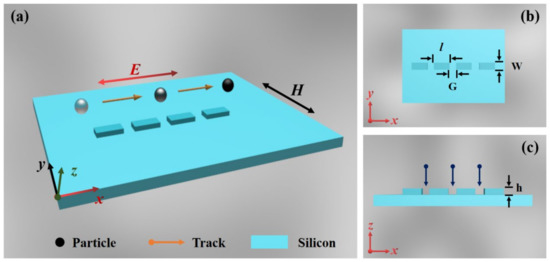
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Effect of Mucilage-Based Edible Coating Enriched with Oregano Essential Oil on Postharvest Quality and Sensorial Attributes of Fresh-Cut Loquat
by
, , , , and
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1387; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081387 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
Due to pulp browning, weight loss, firmness loss, and decay, loquat fruits, and even more minimally processed fruits have a very short post-harvest life. The aim of our study was to evaluate the effect of Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage-based edible coating enriched with oregano
[...] Read more.
Due to pulp browning, weight loss, firmness loss, and decay, loquat fruits, and even more minimally processed fruits have a very short post-harvest life. The aim of our study was to evaluate the effect of Opuntia ficus-indica mucilage-based edible coating enriched with oregano oil on postharvest quality, microbial growth, and sensorial attributes of fresh-cut cv Martorana loquat fruit during cold storage. Fresh-cut loquat fruits were dipped in the mucilage-based solution enriched with oregano essential oil (MO-EC) and in distilled water used as control (CTR). According to our results, the mucilage-based edible coating enriched with oregano oil significantly improved the postharvest life of minimally processed loquat fruits by preserving quality, nutraceutical value, and sensory aspects. MO-EC had a barrier effect on fresh-cut loquat fruit, reducing weight and firmness losses, inhibiting TSS, TA, ascorbic acid content decrease, and enhancing the antioxidant activity until the end of the cold storage period (11 days at 5 °C). Microbiological analysis revealed that coated loquat fruits were characterized by a cell density of spoilage microorganisms 1 Log cycle lower than control fruits. The mucilage-based coating enriched with OEO positively affects the visual appearance of fresh-cut loquat fruits, at the end of the cold storage period, MO-EC samples did indeed report visual ratings that were five times greater than CTR samples. Our research suggests that applying mucilage-based coating enriched with OEO improves peeled loquat fruit shelf-life and allows the producers to sell products that are usually considered unmarketable (fruit with epicarp with large spot areas) to the market.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovations in Active Food Packaging during the Pandemic and into the 'New Normal')
►▼
Show Figures
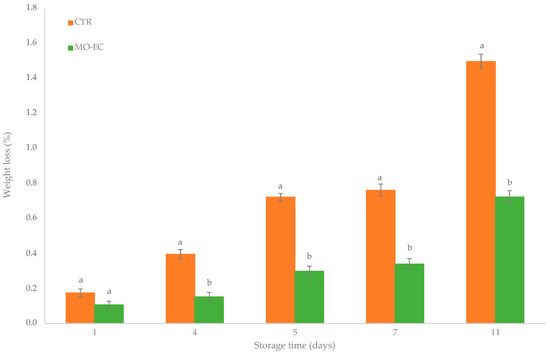
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Preparation and Study of Ca/Tb Co-Doped HfO2 Infrared Coatings with Different Atomic Ratios
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1386; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081386 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this study, HfO2 coatings co-doped with different Ca/Tb atomic ratios were prepared via the atmospheric plasma spraying (APS) method. The microstructure, infrared radiation properties, and high-temperature stability of the coatings were investigated. All of the doped coatings possessed a porous surface
[...] Read more.
In this study, HfO2 coatings co-doped with different Ca/Tb atomic ratios were prepared via the atmospheric plasma spraying (APS) method. The microstructure, infrared radiation properties, and high-temperature stability of the coatings were investigated. All of the doped coatings possessed a porous surface and were composed of two phases, namely the monoclinic HfO2 phase and the cubic HfO2 phase. In addition, the content of the cubic phases increased when raising the doping atomic ratio of Ca/Tb, suggesting that Ca could stabilize the cubic HfO2 phase more effectively. The results also show that the coating with a Ca/Tb atomic ratio of 1/0 (CT1 coating) had more excellent infrared radiative properties, whose total emissivity was 0.844 in the 0.75~6.5 μm band and 0.900 in the 6.5~15 μm band, respectively. The improvement in emissivity in the 0.75~6.5 μm band was mainly due to the impurity energy levels introduced via oxygen vacancy, which promoted the absorption of free carriers. And, in 6.5~15 μm, because the approximate masses of the Ca-O and Tb-O bonds were smaller than that of the Hf-O bonds, the infrared absorption of the lattice vibration shifted, favoring absorption below 10 μm. Moreover, Ca had a more significant strengthening effect than Tb in the whole band. In terms of high-temperature infrared radiation performance, the total emissivity of the CT1 coating at 2.5~25 μm increased as the temperature increased from 500 °C to 1100 °C, which might be attributed to the thermal-enhanced lattice vibration absorption. However, the emissivity of the CT1 coating at 3~5 μm was kept around 0.9 from 1100 °C to 2000 °C, owing to the fact that infrared absorption was more determined by the intrinsic width of the energy levels because of the weakening of the doping effect at high temperatures. In terms of thermal stability, the surface morphology and chemical composition of the CT1 coating were barely changed within 4 h of heat treatment at 2000 °C. The total infrared emissivity of the CT1 coating after 4 h of heat treatment was 0.826 in the 0.75~6.5 μm band and 0.895 in the 6.5~15 μm band, slightly lower than that before heat treatment, suggesting good thermal stability and good application prospects as a high-temperature infrared material.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Metal-Ceramic Composites: Microstructure Tailoring, Properties and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
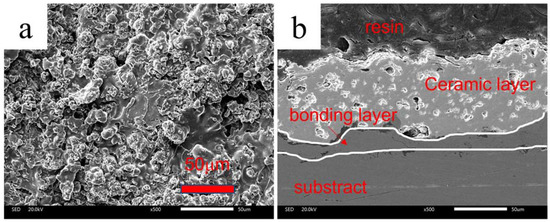
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of the Effect of Additional Zirconium Diboride (ZrB2) in Spherical Graphite Cast Iron on Mechanical Properties
by
and
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1385; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081385 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
Steering gearbox bodies, which are produced from spheroidal graphite cast iron, experience wear and gaps over time since they operate under load. It is important to strengthen steering gearbox bodies to avoid this. In this study, a steering gearbox body was produced from
[...] Read more.
Steering gearbox bodies, which are produced from spheroidal graphite cast iron, experience wear and gaps over time since they operate under load. It is important to strengthen steering gearbox bodies to avoid this. In this study, a steering gearbox body was produced from a spheroidal graphite cast iron material with zirconium diboride at varying rates (0%, 0.227%, 0.455%, and 1.364%). Samples of the material were prepared according to established standards for hardness, compressive strength, and wear resistance tests. The mechanical properties of test samples with and without zirconium diboride (hardness, compressive strength, and wear resistance) were compared. Sample C showed the highest hardness measurement of 243 HB after adding 0.455% zirconium diboride. As the rate of addition increased, the values obtained from the hardness measurement test also increased. Sample C had the highest compressive value of 1438 MPa, with a 0.455% addition rate. It was found that the compressive strength values also increased as the addition rate increased. Wear tests were conducted to analyse wear volume, wear rate, and friction coefficients. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) device was utilised to identify wear mechanisms on the worn surfaces of the samples. Per the results of this study, wear volume values were found to increase with the load value.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Tribological Properties and Wear Protection of Coatings and Alloys)
►▼
Show Figures
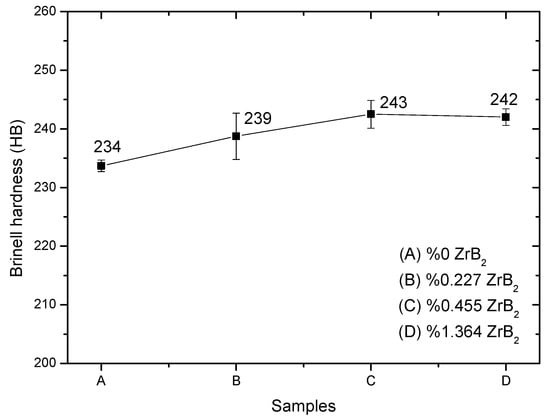
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Insight into the Desolvation of Organic Electrolyte Cations with Propylene Carbonate as a Solvent in Flat Pores: A First-Principles Calculation
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1384; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081384 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Supercapacitors have many applications in new energy and other high-tech fields. The desolvation effect on ions affects the capacity size of supercapacitors, and there are few relevant studies published in this field at present. In this experiment, bilayer graphene (BG) with a layer
[...] Read more.
Supercapacitors have many applications in new energy and other high-tech fields. The desolvation effect on ions affects the capacity size of supercapacitors, and there are few relevant studies published in this field at present. In this experiment, bilayer graphene (BG) with a layer spacing of 4–10 Å was used as a model of flat pores and was calculated with first-principles calculations, which can effectively simulate the adsorption behaviour of porous carbon. The reaction energies of ions, propylene carbonate, and ionic complexes in bilayer graphene with different layer spacings were calculated, and the desolvation behaviour of lithium salt cations (Li+), tetraethyl quaternary ammonium salt cations (TEA+), triethyl methyl quaternary ammonium salt cations (TEMA+), and bipyrrolidinium quaternary ammonium salt cations (SBP+) was investigated. The calculation was based on density functional compact bound (DFTB+) software. The calculated results show that in the stacked system, the complete desolvation size of the TEA+ reaches 5.6 Å, the complete desolvation size of the TEMA+ reaches 4.9 Å, the complete desolvation size of the SBP+ reaches 4.8 Å, and the complete desolvation size of the Li+ reaches 5.4 Å, with the organic electrolyte cations showing a positive trend in the complete desolvation size as the ion radius increases. An in-depth analysis of the data shows that Li+, TEA+, TEMA+, and SBP+ ion radii play a dominant role in the size of desolvation. The results of this paper provide an effective aid for the selection of organic electrolytes to increase the capacity of supercapacitors.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study on Flexural Strength of Interface between Full Lightweight Ceramsite Concrete and Ordinary Concrete
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1383; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081383 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
The efficacy of full lightweight ceramsite concrete as a restorative material has been widely acknowledged, given its light weight, strength, and durability. However, the extent of its performance in repairing existing or old concrete remains uncertain. This study examined the reparation of flexural
[...] Read more.
The efficacy of full lightweight ceramsite concrete as a restorative material has been widely acknowledged, given its light weight, strength, and durability. However, the extent of its performance in repairing existing or old concrete remains uncertain. This study examined the reparation of flexural performance with full lightweight ceramsite concrete, using 14 different combinations of old and new concrete test blocks. The primary focus of the study was on investigating the flexural bond strength of the interface between the old and the new concrete. This included understanding the effects of the interfacial roughness, interfacial agent type, and concrete curing age of the concrete on the flexural strength. The test results showed that increasing the interface roughness from 0 mm to 5 mm resulted a restoration of the flexural strength of the sample by approximately 59%. Additionally, the flexural strength of the specimens was restored by 62%–78% of their original strength with the application of different types of interfacial agent. To rank the impact of these factors on the flexural strength, a univariate analysis of variance was conducted. This allowed us to establish a mathematical formula for calculating the flexural capacity of old and new concrete interfaces, taking the three aforementioned factors into account.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Research in Cement and Building Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Evaluation of Asphalt Mixture Crack Resistance and Identification of Influential Factors
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1382; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081382 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
The crack resistance of asphalt pavement mixtures directly impact pavement service condition and pavement distress. And characterizing the crack resistance of a pavement mixture can reflect the crack resistance potential of asphalt pavement. This study analyzes several representative highway sections based on time,
[...] Read more.
The crack resistance of asphalt pavement mixtures directly impact pavement service condition and pavement distress. And characterizing the crack resistance of a pavement mixture can reflect the crack resistance potential of asphalt pavement. This study analyzes several representative highway sections based on time, material, and service conditions to identify the mixture type of three layers. Semi-circular bending tests are conducted at 15 °C, and load–displacement curves are recorded. Factor independence analysis is performed, and combinations showcasing the cracking performance of the surface layer, middle layer, and bottom layer are selected. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) evaluating the indices versus selected factors for the three layers identifies significant influencing factors, and the crack resistance is analyzed based on these significant factors. The crack resistance of the middle layer with the highest truck loads is significantly lower than the two other lanes and the shoulder. Transverse crack spacing (TCS) can be used to directly evaluate the crack resistance of the mixture. The Factor dots upper rate (FUDR) and absolute Factor dots upper rate (absFUDR) indices are introduced to quantify the percentage deviation of a factor specimen from the average crack resistance index–fracture energy ratio, indicating whether the crack curve becomes sharper or flatter. The factor dots upper rate index is then applied to characterize the factors, and the results are reasonable. It is found only on the surface and middle layers that the service age has significant impacts on crack resistance, the Transverse crack spacing has significant impacts on crack resistance index, and the Factor dots upper rate can identify the brittleness of mixtures with different factors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Surface Engineering and Mechanical Properties of Building Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Structure and Properties of Cermet Coatings Produced by Vacuum-Arc Evaporation of a High-Entropy Alloy
by
, , , , , , and
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1381; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081381 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
Multilayer cermet coatings based on a TiNbZrTaHf high-entropy alloy were produced on solid substrates by plasma-assisted vacuum-arc deposition. The assisting multicomponent metal-gas plasma was generated by evaporating TiNbZrTaHf cathodes in a gas mixture of nitrogen and argon. It was found that the coatings
[...] Read more.
Multilayer cermet coatings based on a TiNbZrTaHf high-entropy alloy were produced on solid substrates by plasma-assisted vacuum-arc deposition. The assisting multicomponent metal-gas plasma was generated by evaporating TiNbZrTaHf cathodes in a gas mixture of nitrogen and argon. It was found that the coatings were nanocrystalline in structure (with nanocrystal sizes ranging from 2.5 to 4 nm). The metallic layer had a body-centered cubic lattice (a = 0.33396 nm), and the ceramic layer had a face-centered cubic lattice (a = 0.44465 nm). Transition layers formed between the substrate and the metallic layer and between the metallic and the ceramic layers were revealed. The hardness of the coatings was 36.7 GPa and their Young’s modulus was 323 GPa.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Electron-Ion-Plasma Technology Applied to Surface Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
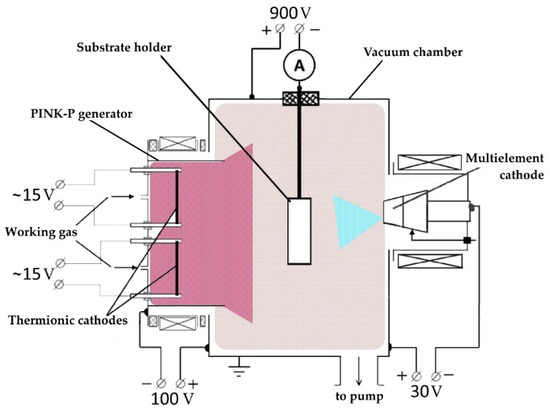
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Effect of Yttrium Addition on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Refractory TiTaZrHfW High-Entropy Films
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1380; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081380 - 07 Aug 2023
Abstract
Refractory high-entropy films (RHEFs) are a new type of high-temperature material with great prospects for applications due to their superior properties. They have the potential to replace nickel-based superalloys in order to develop a new generation of materials that can be used under
[...] Read more.
Refractory high-entropy films (RHEFs) are a new type of high-temperature material with great prospects for applications due to their superior properties. They have the potential to replace nickel-based superalloys in order to develop a new generation of materials that can be used under extreme conditions. (TiTaZrHf)100−xYx RHEFs are prepared using the magnetron sputtering technique. The yttrium (Y) content varies from 0 to 56 at.%. XRD analysis indicates the formation of an amorphous phase in Y-free films, while new phases are formed after the addition of Y. The results are confirmed by TEM analysis, revealing the formation of nano-grains with two phases L12 and Y-P6/mmm structure. With an increasing Y content, the grain size of the nano-grains increases, which has a significant effect on the mechanical properties of the films. Hardness decreases from 9.7 GPa to 5 GPa when the Y amount increases. A similar trend is observed for the Young’s modulus, ranging from 111.6 to 82 GPa. A smooth and featureless morphology is observed on the low Y content films, while those with a larger Y content appear columnar near the substrate. Furthermore, the phase evolution is evaluated by calculating the thermodynamic criteria ΔHmix, ΔSmix, Ω, and δ. The calculation results predict the formation of new phases and are then in good agreement with the experimental characterization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Multielement Coatings: Deposition, Materials and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Electrically Assisted Preheating on Microstructure and Properties of Laser-Cladded Co-Based Coating on CP-Ti Alloy Substrate
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1379; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081379 - 06 Aug 2023
Abstract
Co-based coatings were prepared on commercially pure titanium (CP-Ti) with electrically assisted pre-heating (EAPH), followed by laser cladding with the assistance of pulsed current. Conventional pre-heating (CPH) laser cladding was carried out as a control to investigate the effects of a pulsed current
[...] Read more.
Co-based coatings were prepared on commercially pure titanium (CP-Ti) with electrically assisted pre-heating (EAPH), followed by laser cladding with the assistance of pulsed current. Conventional pre-heating (CPH) laser cladding was carried out as a control to investigate the effects of a pulsed current on the phase composition, microstructure, microhardness, and wear resistance of the coatings. The results showed that periodically varied pulsed currents generate an induced magnetic field. This field fragments bottom dendrites and transforms columnar dendrites into equiaxed crystals through the influence of the Lorentz force. The phase composition of the coatings remained unchanged under the pulsed current, as well as unassisted and CPH condition, consisting of γ-Co, α-Ti, CoTi2 solid solution, and TiC, Cr7C3 hard phases. The microhardness of the coating increased at 720 A due to grain refinement, compared to unassisted and preheated coatings at the same temperature. Moreover, a suitable preheating temperature can reduce crack generation and improve the wear properties of the coating.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Laser Processing of Metallic Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
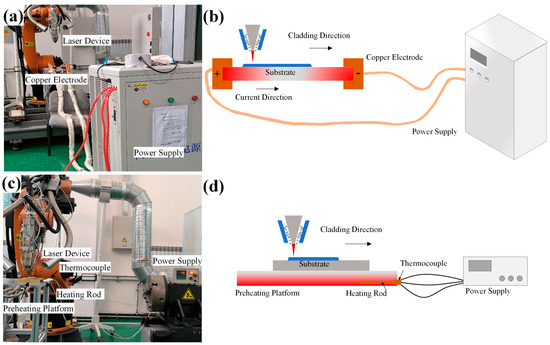
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Simulations of Effects of Geometric and Material Parameters on the Interfacial Stress of the Thermal Barrier Coatings with Free Edges
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1378; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081378 - 06 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Interfacial stress between layers of thermal barrier coatings near free edges is a critical factor that may cause turbine blades to fail. This paper uses simulation methods to reveal the effects of variations in geometric and material parameters on the stress of thermal
[...] Read more.
Interfacial stress between layers of thermal barrier coatings near free edges is a critical factor that may cause turbine blades to fail. This paper uses simulation methods to reveal the effects of variations in geometric and material parameters on the stress of thermal barrier coatings. The stress distributions of a disk-shaped coating–substrate system undergoing thermal mismatch are calculated by an analytical method and the finite element method. The analytical solution reveals that the coefficient of thermal expansion, elasticity modulus, Poisson’s ratio, and thickness of each layer affect interfacial stress between coatings and substrate. The simulation results exhibit significant concentrations of the normal and shear stresses, which make the coating system prone to cracking and spalling from the free edge. The parametric analysis highlights that the thermal mismatch strain affects the stress magnitude. The region affected by free edges becomes larger with increasing thickness, elasticity modulus, and Poisson’s ratio of the topcoat. Finally, two integral parameters are proposed to represent the stress state near the free edge related to mode I and II fracture, respectively. The parameters, not sensitive to the grid density, are validated by experiments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Working Performance and Mechanical Strength of Reactive Powder Concrete with the CO2 Curing Method on the Surface of Secondary Aluminum Ash
Coatings 2023, 13(8), 1377; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13081377 - 05 Aug 2023
Abstract
Secondary aluminum ash (SAA) is a common waste that, without reasonable treatment, results in pollution to the environment. A large amount of CO2 is emitted by human activities every day. If the CO2 cannot be treated in a timely manner, it
[...] Read more.
Secondary aluminum ash (SAA) is a common waste that, without reasonable treatment, results in pollution to the environment. A large amount of CO2 is emitted by human activities every day. If the CO2 cannot be treated in a timely manner, it will accelerate the greenhouse effect and pollute the environment. The CO2 curing on the surface of SAA can reduce excess CO2 emissions while improving the performance of the SAA. The application of CO2-cured SAA can simultaneously consume the emitted CO2 and solidify the SAA. In this article, the effect of CO2-cured secondary aluminum ash on the rheological properties, the initial setting time, the flexural strength (ft), the compressive strength (fcu) of reactive powder concrete (RPC), and the corresponding dry shrinkage rate (DSR) are investigated. Meanwhile, the capillary water absorption, the chloride ion migration coefficient (CMC), and the carbonization depth of RPC are determined. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) and the X-ray diffraction spectrum curves are selected to reveal the mechanism of the macro performance. Results indicate that CO2-cured secondary aluminum ash can increase the fluidity and decrease the plastic viscosity of fresh RPC. The initial setting time is increased by the CO2 curing. CO2-cured secondary aluminum ash can increase the ft and fcu by (0%~26.3% and 0% to 68.7%), respectively. The DSR is increased by adding secondary aluminum ash with an increasing rate of 0% to 91.3%. The capillary water absorption of RPC increases in the form of a linear function. The CMC and the carbonization depth of RPC are decreased by adding the CO2-cured secondary aluminum ash with decreasing rates of 0%~46.7% and 0%~45.7%. The CO2-cured secondary aluminum ash can make the hydration more compact and increased increase the hydration products (Ca(OH)2).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Surface Modified Repairing Materials and Mechanics)
►▼
Show Figures
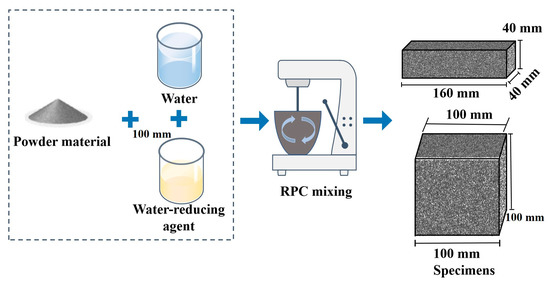
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Coatings Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Coatings, Dentistry Journal, JCM, Materials, Polymers
Advances in Materials and Concepts in Fixed Prosthodontics and Implant Therapy
Topic Editors: Massimo Carossa, Stefano Carossa, Simona Liliana IconaruDeadline: 31 August 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Coatings, JMMP, Materials, Metals
Welding and Joining of Materials in Off-shore and Energy Industry
Topic Editors: Dariusz Fydrych, Jacek Tomków, Aleksandra Świerczyńska, Grzegorz Rogalski, Sergey G. Parshin, Chandan Pandey, Michał Landowski, Hamed Aghajani Derazkola, Thomas HasselDeadline: 15 September 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Coatings, CMD, Materials, Metals
Environmental Sensitivity and Safety Assessment of Materials
Topic Editors: Jian Chen, Daokui Xu, Fanjiang Meng, Jamie NoëlDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Coatings, Electronics, Energies, Sensors, Telecom
Condition Monitoring and Diagnostic Methods for Power Equipment in New Energy Power Systems
Topic Editors: Shuaibing Li, Guoqiang Gao, Guochang Li, Yi Cui, Jiefeng Liu, Guangya Zhu, Jin LiDeadline: 15 October 2023

Conferences
28 May 2023–2 June 2033
The 243rd ECS Meeting and 18th International Symposium on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC-XVIII)

13–16 September 2023
24th International Conference on Advances in Materials & Processing Technologies (AMPT 2023)

19–22 September 2023
14th International Conference on Processes in Isotopes and Molecules (PIM 2023)

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Coatings
Coatings for Building Applications
Guest Editors: Noni-Pagona Maravelaki, Elisa FranzoniDeadline: 10 August 2023
Special Issue in
Coatings
Functional Polymer Films and Their Applications
Guest Editor: Galina K. ElyashevichDeadline: 20 August 2023
Special Issue in
Coatings
Plasmonic Coatings
Guest Editor: Francesco RuffinoDeadline: 31 August 2023
Special Issue in
Coatings
Semiconductor Thin Films
Guest Editor: Nam-Hoon KimDeadline: 23 September 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Coatings
Surface and Interface Science and Engineering for the Society of the Future
Collection Editor: Alessandro Lavacchi
Topical Collection in
Coatings
Advanced Surface Coating of Nanoparticles
Collection Editors: Frank Alexis, Patrick Tang Siah Ying
Topical Collection in
Coatings
Pavement Surface Coatings
Collection Editors: Giuseppe Cantisani, Giuseppe Loprencipe
Topical Collection in
Coatings
Pulsed Laser Deposition of Thin Films: Recent Advances and Challenges
Collection Editors: Emanuel Axente, Gabriel Socol



.jpg)