Journal Description
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
International Journal of Molecular Sciences
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal providing an advanced forum for biochemistry, molecular and cell biology, molecular biophysics, molecular medicine, and all aspects of molecular research in chemistry, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Australian Society of Plant Scientists (ASPS), Epigenetics Society, European Calcium Society (ECS), European Chitin Society (EUCHIS), Spanish Society for Cell Biology (SEBC) and others are affiliated with IJMS and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, MEDLINE, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Biochemistry & Molecular Biology) / CiteScore - Q1 (Inorganic Chemistry)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about the IJMS.
- Companion journals for IJMS include: Biophysica, Obesities, Stresses and Lymphatics.
Impact Factor:
5.6 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
6.2 (2022)
Latest Articles
Evaluation of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Idebenone Responsiveness in Fibroblasts from Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON) Subjects
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12580; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612580 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a disease that affects the optical nerve, causing visual loss. The diagnosis of LHON is mostly defined by the identification of three pathogenic variants in the mitochondrial DNA. Idebenone is widely used to treat LHON patients, but
[...] Read more.
Leber’s hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) is a disease that affects the optical nerve, causing visual loss. The diagnosis of LHON is mostly defined by the identification of three pathogenic variants in the mitochondrial DNA. Idebenone is widely used to treat LHON patients, but only some of them are responders to treatment. In our study, we assessed the maximal respiration rate (MRR) and other respiratory parameters in eight fibroblast lines from subjects carrying LHON pathogenic variants. We measured also the effects of idebenone treatment on cell growth and mtDNA amounts. Results showed that LHON fibroblasts had significantly reduced respiratory parameters in untreated conditions, but no significant gain in MRR after idebenone supplementation. No major toxicity toward mitochondrial function and no relevant compensatory effect in terms of mtDNA quantity were found for the treatment at the tested conditions. Our findings confirmed that fibroblasts from subjects harboring LHON pathogenic variants displayed impaired respiration, regardless of the disease penetrance and severity. Testing responsiveness to idebenone treatment in cultured cells did not fully recapitulate in vivo data. The in-depth evaluation of cellular respiration in fibroblasts is a good approach to evaluating novel mtDNA variants associated with LHON but needs further evaluation as a potential biomarker for disease prognosis and treatment responsiveness.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mitochondrial Medicine: Pharmacological Targeting of Mitochondria in Disease)
Open AccessReview
Regulation of Notch1 Signalling by Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancers and Other Health Disorders
by
, , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12579; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612579 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Notch1 signalling plays a multifaceted role in tissue development and homeostasis. Currently, due to the pivotal role of Notch1 signalling, the relationship between NOTCH1 expression and the development of health disorders is being intensively studied. Nevertheless, Notch1 signalling is not only controlled at
[...] Read more.
Notch1 signalling plays a multifaceted role in tissue development and homeostasis. Currently, due to the pivotal role of Notch1 signalling, the relationship between NOTCH1 expression and the development of health disorders is being intensively studied. Nevertheless, Notch1 signalling is not only controlled at the transcriptional level but also by a variety of post-translational events. First is the ligand-dependent mechanical activation of NOTCH receptors and then the intracellular crosstalk with other signalling molecules—among those are long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). In this review, we provide a detailed overview of the specific role of lncRNAs in the modulation of Notch1 signalling, from expression to activity, and their connection with the development of health disorders, especially cancers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Notch Signaling in Health and Disease 2.0)
Open AccessArticle
Depletion of SNORA33 Abolishes ψ of 28S-U4966 and Affects the Ribosome Translational Apparatus
by
, , , , , , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12578; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612578 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Eukaryotic ribosomes are complex molecular nanomachines translating genetic information from mRNAs into proteins. There is natural heterogeneity in ribosome composition. The pseudouridylation (ψ) of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) is one of the key sources of ribosome heterogeneity. Nevertheless, the functional consequences of ψ-based ribosome
[...] Read more.
Eukaryotic ribosomes are complex molecular nanomachines translating genetic information from mRNAs into proteins. There is natural heterogeneity in ribosome composition. The pseudouridylation (ψ) of ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) is one of the key sources of ribosome heterogeneity. Nevertheless, the functional consequences of ψ-based ribosome heterogeneity and its relevance for human disease are yet to be understood. Using HydraPsiSeq and a chronic disease model of non-osteoarthritic primary human articular chondrocytes exposed to osteoarthritic synovial fluid, we demonstrated that the disease microenvironment is capable of instigating site-specific changes in rRNA ψ profiles. To investigate one of the identified differential rRNA ψ sites (28S-ψ4966), we generated SNORA22 and SNORA33 KO SW1353 cell pools using LentiCRISPRv2/Cas9 and evaluated the ribosome translational capacity by 35S-Met/Cys incorporation, assessed the mode of translation initiation and ribosomal fidelity using dual luciferase reporters, and assessed cellular and ribosomal proteomes by LC-MS/MS. We uncovered that the depletion of SNORA33, but not SNORA22, reduced 28S-ψ4966 levels. The resulting loss of 28S-ψ4966 affected ribosomal protein composition and function and led to specific changes in the cellular proteome. Overall, our pioneering findings demonstrate that cells dynamically respond to disease-relevant changes in their environment by altering their rRNA pseudouridylation profiles, with consequences for ribosome function and the cellular proteome relevant to human disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Non-coding RNA in Physiology and Pathophysiology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Tools for Etiologic Diagnosis of Drug-Induced Allergic Conditions
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12577; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612577 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Drug hypersensitivity reactions are a serious concern in clinical practice because they can be severe and result in lifelong sequelae. An accurate diagnosis and identification of the culprit drug is essential to prevent future reactions as well as for the identification of safe
[...] Read more.
Drug hypersensitivity reactions are a serious concern in clinical practice because they can be severe and result in lifelong sequelae. An accurate diagnosis and identification of the culprit drug is essential to prevent future reactions as well as for the identification of safe treatment alternatives. Nonetheless, the diagnosis can be challenging. In vivo and in vitro tests can be helpful, although none are conclusive; therefore, the tests are not usually performed in isolation but as part of a diagnostic algorithm. In addition, some in vitro tests are only available in research laboratories, and standardization has not been fully accomplished. Collaborating research is needed to improve drug hypersensitivity reaction diagnosis. In this review, we update the current available in vivo and in vitro tools with their pros and cons and propose an algorithm to integrate them into clinical practice.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular and Cellular Advances in Atopic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
DNA Methylation Signatures of Multiple Sclerosis Occur Independently of Known Genetic Risk and Are Primarily Attributed to B Cells and Monocytes
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12576; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612576 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Epigenetic mechanisms can regulate how DNA is expressed independently of sequence and are known to be associated with various diseases. Among those epigenetic mechanisms, DNA methylation (DNAm) is influenced by genotype and the environment, making it an important molecular interface for studying disease
[...] Read more.
Epigenetic mechanisms can regulate how DNA is expressed independently of sequence and are known to be associated with various diseases. Among those epigenetic mechanisms, DNA methylation (DNAm) is influenced by genotype and the environment, making it an important molecular interface for studying disease etiology and progression. In this study, we examined the whole blood DNA methylation profiles of a large group of people with (pw) multiple sclerosis (MS) compared to those of controls. We reveal that methylation differences in pwMS occur independently of known genetic risk loci and show that they more strongly differentiate disease (AUC = 0.85, 95% CI 0.82–0.89, p = 1.22 × 10−29) than known genetic risk loci (AUC = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.66–0.76, p = 9.07 × 10−17). We also show that methylation differences in MS occur predominantly in B cells and monocytes and indicate the involvement of cell-specific biological pathways. Overall, this study comprehensively characterizes the immune cell-specific epigenetic architecture of MS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Mechanism in Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders)
►▼
Show Figures
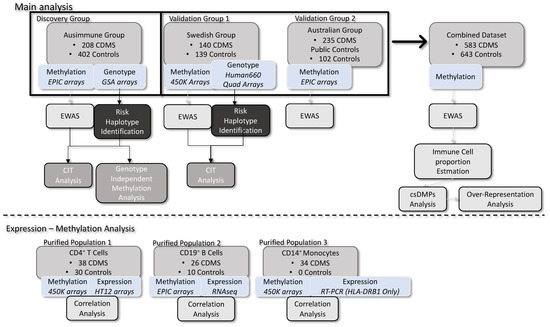
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Catalyst Design through Grafting of Diazonium Salts—A Critical Review on Catalyst Stability
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12575; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612575 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
In the pursuit of designing a reusable catalyst with enhanced catalytic activity, recent studies indicate that electrochemical grafting of diazonium salts is an efficient method of forming heterogeneous catalysts. The aim of this review is to assess the industrial applicability of diazonium-based catalysts
[...] Read more.
In the pursuit of designing a reusable catalyst with enhanced catalytic activity, recent studies indicate that electrochemical grafting of diazonium salts is an efficient method of forming heterogeneous catalysts. The aim of this review is to assess the industrial applicability of diazonium-based catalysts with particular emphasis on their mechanical, chemical, and thermal stability. To this end, different approaches to catalyst production via diazonium salt chemistry have been compared, including the immobilization of catalysts by a chemical reaction with a diazonium moiety, the direct use of diazonium salts and nanoparticles as catalysts, the use of diazonium layers to modulate wettability of a carrier, as well as the possibility of transforming the catalyst into the corresponding diazonium salt. After providing descriptions of the most suitable carriers, the most common deactivation routes of catalysts have been discussed. Although diazonium-based catalysts are expected to exhibit good stability owing to the covalent bond created between a catalyst and a post-diazonium layer, this review indicates the paucity of studies that experimentally verify this hypothesis. Therefore, use of diazonium salts appears a promising approach in catalysts formation if more research efforts can focus on assessing their stability and long-term catalytic performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Heterogeneous Catalysts: Design, Synthesis, and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
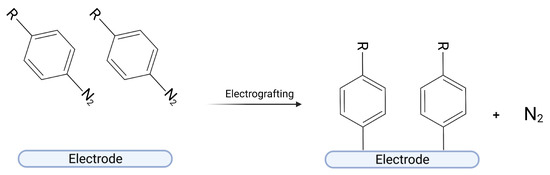
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Common Variants in One-Carbon Metabolism Genes (MTHFR, MTR, MTHFD1) and Depression in Gynecologic Cancers
by
, , , , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12574; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612574 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
We investigated the association between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (gene MTHFR 677C>T, rs1801133), 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase (MTR 2756A>G, rs1805087), and methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, cyclohydrolase and formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase 1 (gene MTHFD1 1958G>A, rs2236225)—well-studied functional variants involved in one-carbon metabolism—and gynecologic cancer risk, and the interaction between these
[...] Read more.
We investigated the association between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (gene MTHFR 677C>T, rs1801133), 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase (MTR 2756A>G, rs1805087), and methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase, cyclohydrolase and formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase 1 (gene MTHFD1 1958G>A, rs2236225)—well-studied functional variants involved in one-carbon metabolism—and gynecologic cancer risk, and the interaction between these polymorphisms and depression. A total of 200 gynecologic cancer cases and 240 healthy controls were recruited to participate in this study. Three single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) (rs1801133, rs1805087, rs2236225) were genotyped using the PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism method. Depression was assessed in all patients using the Hamilton Depression Scale. Depression was statistically significantly more frequent in women with gynecologic cancers (69.5% vs. 34.2% in controls, p < 0.001). MTHFD1 rs2236225 was associated with an increased risk of gynecologic cancers (in dominant OR = 1.53, p = 0.033, and in log-additive models OR = 1.37, p = 0.024). Moreover, an association was found between depression risk and MTHFR rs1801133 genotypes in the controls but not in women with gynecologic cancers (in codominant model CC vs. TT: OR = 3.39, 95%: 1.49–7.74, p = 0.011). Cancers of the female reproductive system are associated with the occurrence of depression, and ovarian cancer may be associated with the rs2236225 variant of the MTHFD1 gene. In addition, in healthy aging women in the Polish population, the rs1801133 variant of the MTHFR gene is associated with depression.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Neurobiology)
►▼
Show Figures
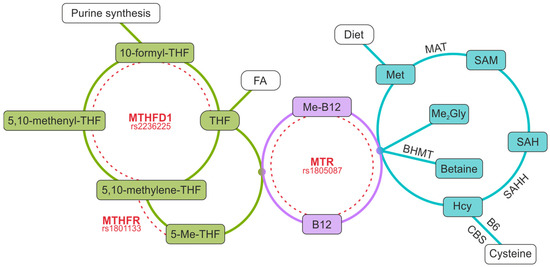
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Purine Nucleotide Alterations in Tumoral Cell Lines Maintained with Physiological Levels of Folic Acid
by
, , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12573; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612573 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Most cancer cells have an increased synthesis of purine nucleotides to fulfil their enhanced division rate. The de novo synthesis of purines requires folic acid in the form of N10-formyltetrahydrofolate (10-formyl-THF). However, regular cell culture media contain very high, non-physiological concentrations
[...] Read more.
Most cancer cells have an increased synthesis of purine nucleotides to fulfil their enhanced division rate. The de novo synthesis of purines requires folic acid in the form of N10-formyltetrahydrofolate (10-formyl-THF). However, regular cell culture media contain very high, non-physiological concentrations of folic acid, which may have an impact on cell metabolism. Using cell culture media with physiological levels of folic acid (25 nM), we uncover purine alterations in several human cell lines. HEK293T, Jurkat, and A549 cells accumulate 5′-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (ZMP), an intermediary of the de novo biosynthetic pathway, at physiological levels of folic acid, but not with the artificially high levels (2200 nM) present in regular media. Interestingly, HEK293T and Jurkat cells do not accumulate high levels of ZMP when AICAr, the precursor of ZMP, is added to medium containing 2200 nM folate; instead, ATP levels are increased, suggesting an enhanced de novo synthesis. On the other hand, HeLa and EHEB cells do not accumulate ZMP at physiological levels of folic acid, but they do accumulate in medium containing AICAr plus 2200 nM folate. Expression of SLC19A1, which encodes the reduced folate carrier (RFC), is increased in HEK293T and Jurkat cells compared with HeLa and EHEB, and it is correlated with the total purine nucleotide content at high levels of folic acid or with ZMP accumulation at physiological levels of folic acid. In conclusion, tumoral cell lines show a heterogenous response to folate changes in the media, some of them accumulating ZMP at physiological levels of folic acid. Further research is needed to clarify the ZMP downstream targets and their impact on cell function.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Biochemistry)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
CFTR Modulates Hypothalamic Neuron Excitability to Maintain Female Cycle
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12572; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612572 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), known as an epithelial Cl− channel, is increasingly noted to be expressed in the nervous system, although whether and how it plays a role in neuronal excitability is unclear. Given the association of CFTR with fertility,
[...] Read more.
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), known as an epithelial Cl− channel, is increasingly noted to be expressed in the nervous system, although whether and how it plays a role in neuronal excitability is unclear. Given the association of CFTR with fertility, we tested here possible involvement of CFTR in regulating hypothalamic neuron excitability. Patch-clamp and Ca2+ imaging showed that pharmacological inhibition of CFTR evoked electrical pulses and Ca2+ spikes in primary rat hypothalamic neurons, which was dependent on extracellular Cl−. Hypothalamic neurons in brain-slice preparations from adult female mice with CFTR mutation (DF508) exhibited significantly reduced electrical pulses as compared to the wild-type controls. Removal of extracellular Cl− eliminated hypothalamic electrical pulses in the wild-type brain slices, which was reversible by subsequent addition of Cl−. In adult female mice, Ca2+ indicator (GCaMP6s)-based fiber-photometry showed that hypothalamic Ca2+ activities in vivo were enhanced at the proestrus/estrus phase as compared to the diestrus phase of the female cycle. Such estrus-associated hypothalamic activities were largely diminished in DF508 female mice, together with delayed puberty and disturbed female cycles. Therefore, these findings suggest a critical role of CFTR in modulating hypothalamic neuron excitability, which may account for the disturbed female cycles and reduced female fertility associated with CFTR mutations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Ion Channels and Biosignal Transduction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of the JAK/STAT Inhibitor Tofacitinib on Macrophage Cholesterol Metabolism
by
, , , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12571; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612571 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The impact of JAK/STAT inhibitors, which are used in various inflammatory diseases, on cardiovascular risk is controversial and has recently raised safety concerns. Our study investigates the direct effects of tofacitinib on macrophage cholesterol metabolism, which is crucial for atherosclerosis plaque development and
[...] Read more.
The impact of JAK/STAT inhibitors, which are used in various inflammatory diseases, on cardiovascular risk is controversial and has recently raised safety concerns. Our study investigates the direct effects of tofacitinib on macrophage cholesterol metabolism, which is crucial for atherosclerosis plaque development and stability. Cultured human macrophages THP-1 were used to assess the impact of tofacitinib on cell cholesterol efflux and synthesis via radioisotopic methods, and on cholesterol uptake by measuring the cell cholesterol content with a fluorometric assay. The cholesterol acceptors and donors were either standard lipoproteins or sera from patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and from control subjects. Tofacitinib significantly increased the macrophage cholesterol efflux to all acceptors; it reduced cholesterol uptake from both the normal and hypercholesterolemic sera; and it reduced cholesterol synthesis. The treatment of macrophages with tofacitinib was able to increase the cholesterol efflux and decrease cholesterol uptake when using sera from untreated JIA patients with active disease as cholesterol acceptors and donors, respectively. In conclusion, our in vitro data support the concept that tofacitinib has a favorable impact on macrophage cholesterol metabolism, even in the presence of sera from rheumatologic patients, and suggest that other mechanisms may be responsible for the cardiovascular risk associated with tofacitinib use in selected patient populations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Atherosclerosis: From Molecular Biology to Therapeutic Perspective 4.0)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
APE-1/Ref-1 Inhibition Blocks Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cell Proliferation and Migration: Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Driving Carcinogenesis and Metastasis
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12570; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612570 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive cancer associated with asbestos exposure. MPM pathogenesis has been related both to oxidative stress, evoked by and in response to asbestos fibers exposure, and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), an event induced by oxidative stress itself and
[...] Read more.
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive cancer associated with asbestos exposure. MPM pathogenesis has been related both to oxidative stress, evoked by and in response to asbestos fibers exposure, and epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), an event induced by oxidative stress itself and related to cancer proliferation and metastasis. Asbestos-related primary oxidative damage is counteracted in the lungs by various redox-sensitive factors, often hyperactivated in some cancers. Among these redox-sensitive factors, Apurinic-apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE-1)/Redox effector factor 1 (Ref-1) has been demonstrated to be overexpressed in MPM and lung cancer, but the molecular mechanism has not yet been fully understood. Moreover, asbestos exposure has been associated with induced EMT events, via some EMT transcription factors, such as Twist, Zeb-1 and Snail-1, in possible crosstalk with oxidative stress and inflammation events. To demonstrate this hypothesis, we inhibited/silenced Ref-1 in MPM cells; as a consequence, both EMT (Twist, Zeb-1 and Snail-1) markers and cellular migration/proliferation were significantly inhibited. Taken as a whole, these results show, for the first time, crosstalk between oxidative stress and EMT in MPM carcinogenesis and invasiveness, thus improving the knowledge to better address a preventive and therapeutic approach against this aggressive cancer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Tumor Targeting Theranostics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Histone Deacetylase HstD Regulates Fungal Growth, Development and Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis in Aspergillus terreus
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12569; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612569 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Histone acetylation modification significantly affects secondary metabolism in filamentous fungi. However, how histone acetylation regulates secondary metabolite synthesis in the lovastatin (a lipid-lowering drug) producing Aspergillus terreus remains unknown because protein is involved and has been identified in this species. Here, the fungal-specific
[...] Read more.
Histone acetylation modification significantly affects secondary metabolism in filamentous fungi. However, how histone acetylation regulates secondary metabolite synthesis in the lovastatin (a lipid-lowering drug) producing Aspergillus terreus remains unknown because protein is involved and has been identified in this species. Here, the fungal-specific histone deacetylase gene, hstD, was characterized through functional genomics in two marine-derived A. terreus strains, Mj106 and RA2905. The results showed that the ablation of HstD resulted in reduced mycelium growth, less conidiation, and decreased lovastatin biosynthesis but significantly increased terrein biosynthesis. However, unlike its homologs in yeast, HstD was not required for fungal responses to DNA damage agents, indicating that HstD likely plays a novel role in the DNA damage repair process in A. terreus. Furthermore, the loss of HstD resulted in a significant upregulation of H3K56 and H3K27 acetylation when compared to the wild type, suggesting that epigenetic functions of HstD, as a deacetylase, target H3K27 and H3K56. Additionally, a set of no-histone targets with potential roles in fungal growth, conidiation, and secondary metabolism were identified for the first time using acetylated proteomic analysis. In conclusion, we provide a comprehensive analysis of HstD for its targets in histone or non-histone and its roles in fungal growth and development, DNA damage response, and secondary metabolism in A. terreus.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Molecular Microbiology)
►▼
Show Figures
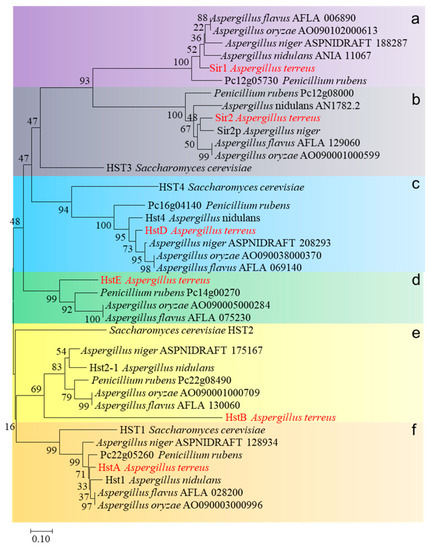
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Structure Properties of Carbon Materials Formed in 2,4,6-Triamino-1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene Detonation: A Theoretical Insight for Nucleation of Diamond-like Carbon
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12568; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612568 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The structure and properties of nano-carbon materials formed in explosives detonation are always a challenge, not only for the designing and manufacturing of these materials but also for clearly understanding the detonation performance of explosives. Herein, we study the dynamic evolution process of
[...] Read more.
The structure and properties of nano-carbon materials formed in explosives detonation are always a challenge, not only for the designing and manufacturing of these materials but also for clearly understanding the detonation performance of explosives. Herein, we study the dynamic evolution process of condensed-phase carbon involved in 2,4,6-Triamino-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene (TATB) detonation using the quantum-based molecular dynamics method. Various carbon structures such as, graphene-like, diamond-like, and “diaphite”, are obtained under different pressures. The transition from a C sp2- to a sp3-hybrid, driven by the conversion of a hexatomic to a non-hexatomic ring, is detected under high pressure. A tightly bound nucleation mechanism for diamond-like carbon dominated by a graphene-like carbon layer is uncovered. The graphene-like layer is readily constructed at the early stage, which would connect with surrounding carbon atoms or fragments to form the tetrahedral structure, with a high fraction of sp3-hybridized carbon. After that, the deformed carbon layers further coalesce with each other by bonding between carbon atoms within the five-member ring, to form the diamond-like nucleus. The complex “diaphite” configuration is detected during the diamond-like carbon nucleation, which illustrates that the nucleation and growth of detonation nano-diamond would accompany the intergrowth of graphene-like layers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Chemistry and Chemical Physics)
►▼
Show Figures
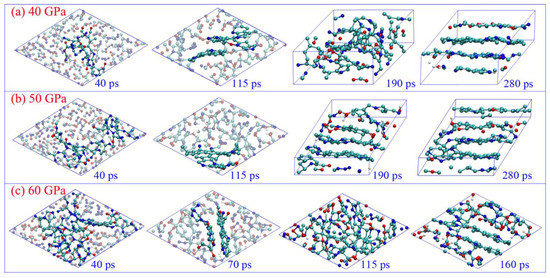
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Molecular Mechanisms of Synaptic Plasticity: Dynamic Changes in Neuron Functions
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12567; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612567 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The human brain has hundreds of billions of neurons and at least 7 million dendrites have been hypothesized to exist for each neuron, with over 100 trillion neuron–neuron, neuron–muscle, and neuron–endocrine cell synapses [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Mechanisms of Synaptic Plasticity: Dynamic Changes in Neurons Functions)
Open AccessArticle
GV1001 Inhibits the Severity of the Ligature-Induced Periodontitis and the Vascular Lipid Deposition Associated with the Periodontitis in Mice
by
, , , , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12566; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612566 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
GV1001, a 16 amino acid peptide derived from the catalytic segment of human telomerase reverse transcriptase, was developed as an anti-cancer vaccine. Subsequently, it was found to exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-Alzheimer’s disease properties. Periodontitis is a risk factor for a variety of systemic
[...] Read more.
GV1001, a 16 amino acid peptide derived from the catalytic segment of human telomerase reverse transcriptase, was developed as an anti-cancer vaccine. Subsequently, it was found to exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-Alzheimer’s disease properties. Periodontitis is a risk factor for a variety of systemic diseases, including atherosclerosis, a process in which chronic systemic and vascular inflammation results in the formation of plaques containing lipids, macrophages, foam cells, and tissue debris on the vascular intima. Thus, we investigated the effect of GV1001 on the severity of ligature-induced periodontitis, vascular inflammation, and arterial lipid deposition in mice. GV1001 notably reduced the severity of ligature-induced periodontitis by inhibiting gingival and systemic inflammation, alveolar bone loss, and vascular inflammation in wild-type mice. It also significantly lowered the amount of lipid deposition in the arterial wall in ApoE-deficient mice receiving ligature placement without changing the serum lipid profile. In vitro, we found that GV1001 inhibited the Receptor Activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast formation and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)-induced phenotypic changes in endothelial cells. In conclusion, our study suggests that GV1001 prevents the exacerbation of periodontitis and atherosclerosis associated with periodontitis partly by inhibiting local, systemic, and vascular inflammation and phenotypic changes of vascular endothelial cells.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Periodontal Disease, Association with Systemic Conditions and Periodontal Pathogens)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Branched DNA-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Sensitive Nucleic Acids Analysis with Gold Nanoparticles as Amplifier
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12565; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612565 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
A branched DNA-based electrochemical biosensor was designed to sensitively detect specific nucleic acids. On this platform, novel a branched DNA with three sticky ends could be used as a biosensor to sensitively and specifically detect nucleic acids. Meanwhile, we also employed branched DNA-modified
[...] Read more.
A branched DNA-based electrochemical biosensor was designed to sensitively detect specific nucleic acids. On this platform, novel a branched DNA with three sticky ends could be used as a biosensor to sensitively and specifically detect nucleic acids. Meanwhile, we also employed branched DNA-modified AuNPs as a signal amplifier to further improve the sensitivity. Branched DNA sensors, target DNA, and DNA-modified AuNPs formed a sandwich structure to produce an electronic signal for target DNA detection. The reaction primarily involved DNA hybridization without bulky thermal cyclers and enzymes. We proved that the hybridization reaction easily occurred under different conditions, such as the NaCl concentration, reaction time, pH, and temperature, except for a pH lower than 4. The limit of detection could go as low as 0.09 pM (S/N = 3) with excellent specificity and selectivity. There was a correlation curve relationship between the peak current and the logarithm of the target DNA concentration (0.10 pM to 10 nM). The correlation coefficient reached 0.987. The electrochemical platform enables a branched DNA nanostructure to determine nucleic acids for disease diagnosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Feature Paper Collection in Biochemistry)
►▼
Show Figures
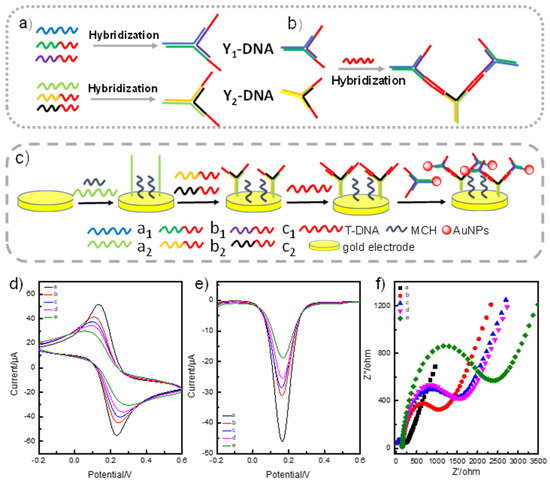
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Neuroinflammation Profiling of Brain Cytokines Following Repeated Blast Exposure
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12564; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612564 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Due to use of explosive devices and heavy weapons systems in modern conflicts, the effect of BW on the brain and body is of increasing concern. These exposures have been commonly linked with neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders in veteran populations. A likely
[...] Read more.
Due to use of explosive devices and heavy weapons systems in modern conflicts, the effect of BW on the brain and body is of increasing concern. These exposures have been commonly linked with neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders in veteran populations. A likely neurobiological link between exposure to blasts and the development of neurobehavioral disorders, such as depression and PTSD, could be neuroinflammation triggered by the blast wave. In this study, we exposed rats to single or repeated BW (up to four exposures—one per day) at varied intensities (13, 16, and 19 psi) to mimic the types of blast exposures that service members may experience in training and combat. We then measured a panel of neuroinflammatory markers in the brain tissue with a multiplex cytokine/chemokine assay to understand the pathophysiological process(es) associated with single and repeated blast exposures. We found that single and repeated blast exposures promoted neuroinflammatory changes in the brain that are similar to those characterized in several neurological disorders; these effects were most robust after 13 and 16 psi single and repeated blast exposures, and they exceeded those recorded after 19 psi repeated blast exposures. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-10 were changed by 13 and 16 psi single and repeated blast exposures. In conclusion, based upon the growing prominence of negative psychological health outcomes in veterans and soldiers with a history of blast exposures, identifying the molecular etiology of these disorders, such as blast-induced neuroinflammation, is necessary for rationally establishing countermeasures and treatment regimens.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Metabolic Regulators of Psychological Stress and Brain Trauma)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Crossroads of the Coagulation System and the Immune System: Interactions and Connections
by
, , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12563; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612563 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The coagulation and immune systems, two vital systems in the human body, share intimate connections that fundamentally determine patient health. These systems work together through several common regulatory pathways, including the Tissue Factor (TF) Pathway. Immune cells expressing TF and producing pro-inflammatory cytokines
[...] Read more.
The coagulation and immune systems, two vital systems in the human body, share intimate connections that fundamentally determine patient health. These systems work together through several common regulatory pathways, including the Tissue Factor (TF) Pathway. Immune cells expressing TF and producing pro-inflammatory cytokines can influence coagulation, while coagulation factors and processes reciprocally impact immune responses by activating immune cells and controlling their functions. These shared pathways contribute to maintaining health and are also involved in various pathological conditions. Dysregulated coagulation, triggered by infection, inflammation, or tissue damage, can result in conditions such as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Concurrently, immune dysregulation may lead to coagulation disorders and thrombotic complications. This review elucidates these intricate interactions, emphasizing their roles in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases and cancer. Understanding the complex interplay between these systems is critical for disease management and the development of effective treatments. By exploring these common regulatory mechanisms, we can uncover innovative therapeutic strategies targeting these intricate disorders. Thus, this paper presents a comprehensive overview of the mutual interaction between the coagulation and immune systems, highlighting its significance in health maintenance and disease pathology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hemostasis, Thrombosis, and Immunothrombosis)
►▼
Show Figures
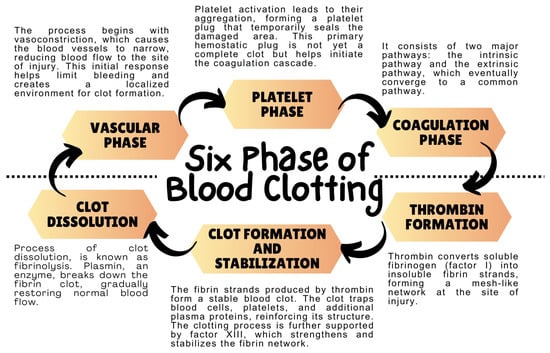
Figure 1
Open AccessCommunication
Difunctional Magnetic Nanoparticles Employed in Immunochromatographic Assay for Rapid and Quantitative Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigen
by
, , , , , , , and
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12562; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612562 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Immunochromatographic assay (ICA) plays an important role in in vitro diagnostics because of its simpleness, convenience, fastness, sensitivity, accuracy, and low cost. The employment of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), possessing both excellent optical properties and magnetic separation functions, can effectively promote the performances of
[...] Read more.
Immunochromatographic assay (ICA) plays an important role in in vitro diagnostics because of its simpleness, convenience, fastness, sensitivity, accuracy, and low cost. The employment of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), possessing both excellent optical properties and magnetic separation functions, can effectively promote the performances of ICA. In this study, an ICA based on MNPs (MNP–ICA) has been successfully developed for the sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). The magnetic probes were prepared by covalently conjugating carboxylated MNPs with the specific monoclonal antibody against CEA, which were not only employed to enrich and extract CEA from serum samples under an external magnetic field but also used as a signal output with its inherent optical property. Under the optimal parameters, the limit of detection (LOD) for qualitative detection with naked eyes was 1.0 ng/mL, and the quantitative detection could be realized with the help of a portable optical reader, indicating that the ratio of optical signal intensity correlated well with CEA concentration ranging from 1.0 ng/mL to 64.0 ng/mL (R2 = 0.9997). Additionally, method comparison demonstrated that the magnetic probes were beneficial for sensitivity improvement due to the matrix effect reduction after magnetic separation, and the MNP–ICA is eight times higher sensitive than ICA based on colloidal gold nanoparticles. The developed MNP–ICA will provide sensitive, convenient, and efficient technical support for biomarkers rapid screening in cancer diagnosis and prognosis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Protein Biosensors)
►▼
Show Figures
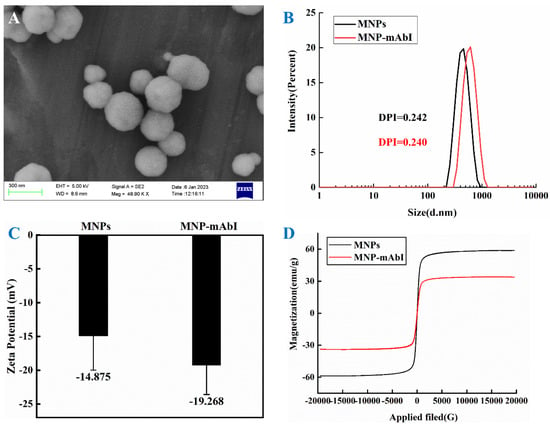
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Classification of Promoter Sequences from Human Genome
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(16), 12561; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241612561 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
We have developed a new method for promoter sequence classification based on a genetic algorithm and the MAHDS sequence alignment method. We have created four classes of human promoters, combining 17,310 sequences out of the 29,598 present in the EPD database. We searched
[...] Read more.
We have developed a new method for promoter sequence classification based on a genetic algorithm and the MAHDS sequence alignment method. We have created four classes of human promoters, combining 17,310 sequences out of the 29,598 present in the EPD database. We searched the human genome for potential promoter sequences (PPSs) using dynamic programming and position weight matrices representing each of the promoter sequence classes. A total of 3,065,317 potential promoter sequences were found. Only 1,241,206 of them were located in unannotated parts of the human genome. Every other PPS found intersected with either true promoters, transposable elements, or interspersed repeats. We found a strong intersection between PPSs and Alu elements as well as transcript start sites. The number of false positive PPSs is estimated to be 3 × 10−8 per nucleotide, which is several orders of magnitude lower than for any other promoter prediction method. The developed method can be used to search for PPSs in various eukaryotic genomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Feature Papers in Molecular Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- IJMS Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Vol. 24 (2023)
- Vol. 23 (2022)
- Vol. 22 (2021)
- Vol. 21 (2020)
- Vol. 20 (2019)
- Vol. 19 (2018)
- Vol. 18 (2017)
- Vol. 17 (2016)
- Vol. 16 (2015)
- Vol. 15 (2014)
- Vol. 14 (2013)
- Vol. 13 (2012)
- Vol. 12 (2011)
- Vol. 11 (2010)
- Vol. 10 (2009)
- Vol. 9 (2008)
- Vol. 8 (2007)
- Vol. 7 (2006)
- Vol. 6 (2005)
- Vol. 5 (2004)
- Vol. 4 (2003)
- Vol. 3 (2002)
- Vol. 2 (2001)
- Vol. 1 (2000)
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Biomolecules, IJMS, Molecules, Sci. Pharm., Cancers, Marine Drugs
Antitumor Activity of Natural Products and Related Compounds
Topic Editors: Barbara De Filippis, Alessandra Ammazzalorso, Marialuigia FantacuzziDeadline: 31 August 2023
Topic in
Energies, IJMS, Membranes, Separations, Water
Membrane Separation Technology Research
Topic Editors: Chenxiao Jiang, Zhe Yang, Ying MeiDeadline: 15 September 2023
Topic in
Biomolecules, Cells, CIMB, IJMS, JMP, Molecules, Proteomes
Metalloproteins and Metalloenzymes
Topic Editors: Eugene A. Permyakov, Ludmilla Morozova-RocheDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Cells, Epigenomes, Genes, IJMS, IJTM
Stem Cell Differentiation and Applications
Topic Editors: Hiroyuki Hirai, Haiyun Pei, Atsushi AsakuraDeadline: 20 October 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
IJMS
Immune Response to Cerebral Ischemia: Exploring Mechanisms and Potential Treatment Targets
Guest Editor: Maria Consuelo BurgueteDeadline: 10 August 2023
Special Issue in
IJMS
Stress-Related Disorders and Depression: From Molecular Basis to Therapy
Guest Editors: Irena Nalepa, Agnieszka Zelek-MolikDeadline: 15 August 2023
Special Issue in
IJMS
New Perspectives in Molecular Diagnosis of Neuromuscular Disorders
Guest Editor: Annalaura TorellaDeadline: 31 August 2023
Special Issue in
IJMS
Silicon-Based Solutions for the Mitigation of Abiotic and Biotic Stresses in Plants
Guest Editor: Gea GuerrieroDeadline: 10 September 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
IJMS
Feature Papers in Bioactives and Nutraceuticals
Collection Editor: Maurizio Battino
Topical Collection in
IJMS
State-of-the-Art Molecular Microbiology in Poland
Collection Editors: Alicja Wegrzyn, Satish Raina
Topical Collection in
IJMS
Computational, Structural and Spectroscopic Studies of Enzyme Mechanisms, Inhibition and Dynamics
Collection Editor: Christo Christov