-
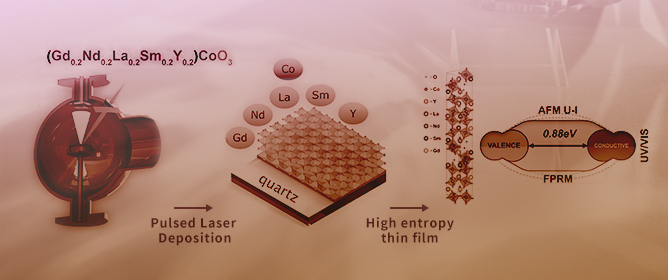 High-Entropy Perovskite Thin Film in the Gd-Nd-Sm-La-Y-Co System: Deposition, Structure and Optoelectronic Properties
High-Entropy Perovskite Thin Film in the Gd-Nd-Sm-La-Y-Co System: Deposition, Structure and Optoelectronic Properties -
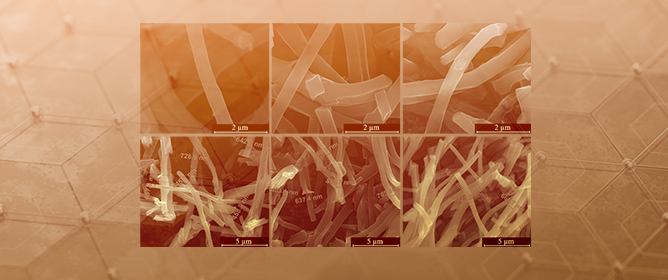 Iron, Cobalt, and Nickel Phthalocyanine Tri-Doped Electrospun Carbon Nanofibre-Based Catalyst for Rechargeable Zinc–Air Battery Air Electrode
Iron, Cobalt, and Nickel Phthalocyanine Tri-Doped Electrospun Carbon Nanofibre-Based Catalyst for Rechargeable Zinc–Air Battery Air Electrode -
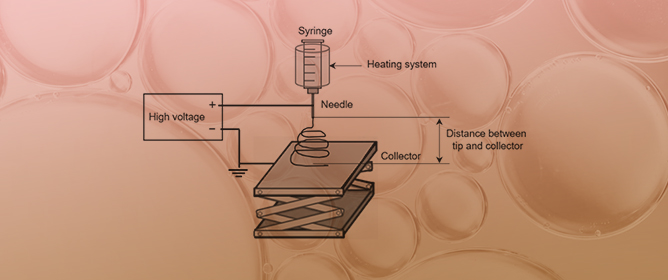 Preparation and Characterization of Crosslinked Electrospun Gelatin Fabrics via Maillard Reactions
Preparation and Characterization of Crosslinked Electrospun Gelatin Fabrics via Maillard Reactions -
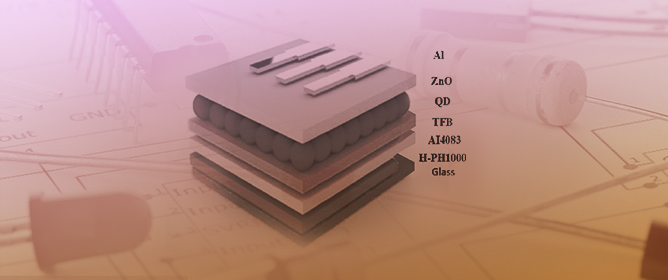 Highly Efficient ITO-Free Quantum-Dot Light Emitting Diodes via Solution-Processed PEDOT:PSS Semitransparent Electrode
Highly Efficient ITO-Free Quantum-Dot Light Emitting Diodes via Solution-Processed PEDOT:PSS Semitransparent Electrode -
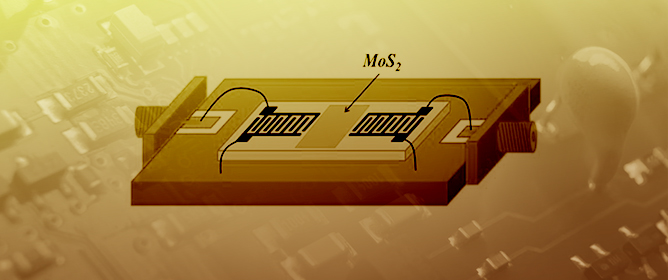 Preparation of MoS2 Nanospheres using a Hydrothermal Method and Their Application as Ammonia Gas Sensors Based on Delay Line Surface Acoustic Wave Devices
Preparation of MoS2 Nanospheres using a Hydrothermal Method and Their Application as Ammonia Gas Sensors Based on Delay Line Surface Acoustic Wave Devices
Journal Description
Materials
Materials
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of materials science and engineering published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Portuguese Materials Society (SPM), Spanish Materials Society (SOCIEMAT) and Manufacturing Engineering Society (MES) are affiliated with Materials and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Ei Compendex, CaPlus / SciFinder, Inspec, Astrophysics Data System, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) / CiteScore - Q2 (Condensed Matter Physics)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 25 topical sections.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Materials.
- Companion journals for Materials include: Electronic Materials and Construction Materials.
Impact Factor:
3.4 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.8 (2022)
Latest Articles
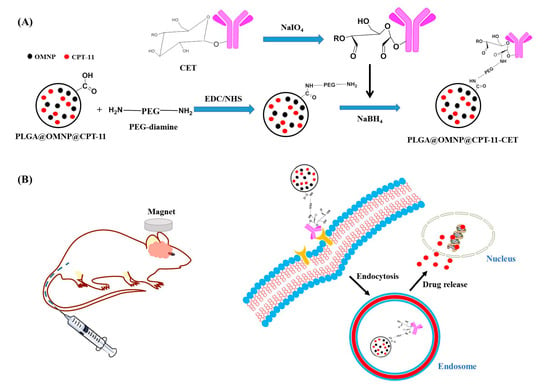
Cetuximab-Conjugated Magnetic Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Nanoparticles for Dual-Targeted Delivery of Irinotecan in Glioma Treatment
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5526; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165526 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
A glioma is the most common malignant primary brain tumor in adults and is categorized according to its growth potential and aggressiveness. Within gliomas, grade 4 glioblastoma remains one of the most lethal malignant solid tumors, with a median survival time less than
[...] Read more.
A glioma is the most common malignant primary brain tumor in adults and is categorized according to its growth potential and aggressiveness. Within gliomas, grade 4 glioblastoma remains one of the most lethal malignant solid tumors, with a median survival time less than 18 months. By encapsulating CPT-11 and oleic acid-coated magnetic nanoparticles (OMNPs) in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles, we first prepared [email protected]@CPT-11 nanoparticles in this study. After conjugating cetuximab (CET) with [email protected]@CPT-11, spherical [email protected]@CPT-11-CET nanoparticles with 250 nm diameter, 33% drug encapsulation efficiency, and 22% drug loading efficiency were prepared in a single emulsion/evaporation step. The nanoparticles were used for dual-targeted delivery of CPT-11 to U87 primary glioblastoma cells by actively targeting the overexpressed epidermal growth factor receptor on the surface of U87 cells, as well as by magnetic targeting. The physicochemical properties of nanoparticles were characterized in detail. CET-mediated targeting promotes intracellular uptake of nanoparticles by U87 cells, which can release four times more drug at pH 5 than at pH 7.4 to facilitate drug release in endosomes after intracellular uptake. The nanovehicle [email protected] is cytocompatible and hemocompatible. After loading CPT-11, [email protected]@CPT-11-CET shows the highest cytotoxicity toward U87 compared with free CPT-11 and [email protected]@CPT-11 by providing the lowest drug concentration for half-maximal cell death (IC50) and the highest rate of cell apoptosis. In orthotopic brain tumor-bearing nude mice with U87 xenografts, intravenous injection of [email protected]@ CPT-11-CET followed by guidance with a magnetic field provided the best treatment efficacy with the lowest tumor-associated signal intensity from bioluminescence imaging.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Functional Magnetic Nanomaterials)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Influence of Metakaolin and Polypropylene Fiber Concrete on Mechanics Properties and Microstructure Combined Action under Multi-Salt Soaking and Freeze–Thaw
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5525; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165525 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The wide distribution of alpine saline areas in China is faced with two major problems, which are salt intrusion and freeze–thaw. In total, 216 specimens were prepared with 6 kinds of concrete mix proportions in this paper. The effects of the single and
[...] Read more.
The wide distribution of alpine saline areas in China is faced with two major problems, which are salt intrusion and freeze–thaw. In total, 216 specimens were prepared with 6 kinds of concrete mix proportions in this paper. The effects of the single and compound incorporation of metakaolin (MK) and polypropylene fiber (PPF) of different amounts on the mechanical properties and microstructure properties of concrete were investigated under the dual action of multi-salt (NaCl, MgCl2, Na2SO4, and NaHCO3) soaking and freeze–thaw. Potable water and freeze–thaw concrete were adopted as the control group. Changes in the appearance morphology, mass loss, relative dynamic elastic modulus, and compressive strength of the concrete were tested, and the microstructure of the concrete was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results showed that an admixture of both MK and PPF in the potable water and freeze–thaw cycle test can improve the mechanical properties and frost resistance of concrete. The admixture of PPF can effectively improve the mechanical properties and frost resistance of concrete. However, the admixture of MK failed to improve the mechanical properties and frost resistance of concrete during multi-salt soaking and freeze–thaw. The frost resistance of concrete under multi-salt soaking and freeze–thaw was optimally improved with 10% MK and 0.6 kg/m3 PPF. Its microstructure shows that PPF can effectively inhibit crack propagation and reduce the deterioration of concrete under multi-salt soaking and freeze–thaw.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Properties and Applications of Cement-based Composites)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Using the LCA Method to Develop the Production of Pigment for Processing Plastics
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5524; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165524 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
In recent years, the chemical industry has been developing more and more dynamically, which results in the introduction of many new chemical substances to the market. However, some of them do not meet the accepted standards and may be toxic to humans and
[...] Read more.
In recent years, the chemical industry has been developing more and more dynamically, which results in the introduction of many new chemical substances to the market. However, some of them do not meet the accepted standards and may be toxic to humans and the environment. This problem largely concerns polymer materials, which are currently widely used in many areas of the economy. This is indirectly related to the coloring of these materials during processing. Therefore, it became necessary to introduce modern research procedures that enable the quantitative and qualitative determination of the impact of coloring agents in the processing of plastics, in order to include their negative impact on humans and the natural environment. The LCA methodology was used in this work, with ReCiPe 2016 used as the test method. Among the analyzed technological operations, the highest negative impact on the environment was characterized by the process related to heating the tested material (2.08 × 10−1 Pt). Among the materials, polyethylene terephthalate was distinguished by the greatest harmful effect on human health (2.91 × 10−1 Pt) and the quality (2.35 × 10−2 Pt) of the environment. The use of recycling processes would reduce the negative impact on human health (about −3.71 Pt), the ecosystem (about −0.14 Pt), and resources (about −0.27 Pt).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Designs of Materials, Machines and Processes in a Circular Economy)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
SPR Sensor Based on a Concave Photonic Crystal Fiber Structure with MoS2/Au Layers
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5523; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165523 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
We propose a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor based on the concave photonic crystal fiber (PCF) coated with molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) and Au layers, which can detect the refractive index (RI) of the analyte. The finite element method (FEM) was used
[...] Read more.
We propose a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor based on the concave photonic crystal fiber (PCF) coated with molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) and Au layers, which can detect the refractive index (RI) of the analyte. The finite element method (FEM) was used to verify our design, and the loss spectra of the fundamental mode are calculated. Compared with the SPR sensor with only a Au layer, the wavelength sensitivity can be improved by from 3700 to 4400 nm/RIU. Our proposed sensor works in near-infrared band and has a wide RI range from 1.19 to 1.40. The influences of the geometrical parameters of PCF and the thicknesses of Au and MoS2 layers on the loss spectra are discussed in detail, and the maximum wavelength sensitivity of 5100 nm/RIU can be achieved. Meanwhile, a high resolution of 1.96 × 10−5 RIU and the largest FOM of 29.143 can be obtained. It is believed that our findings show the sensor’s excellent potential in medical testing, unknown biological detection, environmental monitoring and organic chemical detection.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Atomic Layer Deposition of Titanium Oxide-Based Films for Semiconductor Applications—Effects of Precursor and Operating Conditions
by
, , , , , , and
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5522; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165522 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Two widely used atomic layer deposition precursors, Tetrakis (dimethylamido) titanium (TDMA-Ti) and titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), were investigated for use in the deposition of TiOx-based thin films as a passivating contact material for solar cells. This study revealed that both precursors are
[...] Read more.
Two widely used atomic layer deposition precursors, Tetrakis (dimethylamido) titanium (TDMA-Ti) and titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), were investigated for use in the deposition of TiOx-based thin films as a passivating contact material for solar cells. This study revealed that both precursors are suited to similar deposition temperatures (150 °C). Post-deposition annealing plays a major role in optimising the titanium oxide (TiOx) film passivation properties, improving minority carrier lifetime (τeff) by more than 200 µs. Aluminium oxide deposited together with titanium oxide (AlOy/TiOx) reduced the sheet resistance by 40% compared with pure TiOx. It was also revealed that the passivation quality of the (AlOy/TiOx) stack depends on the precursor and ratio of AlOy to TiOx deposition cycles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Thin Films and 2D Materials: Mechanism, Fabrication, Characterization and Application)
►▼
Show Figures
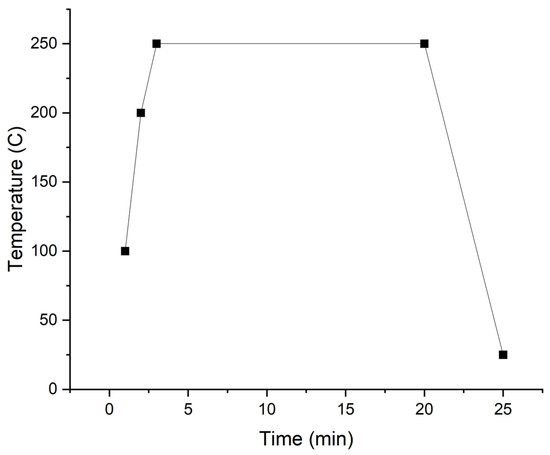
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dewatering of Juglans mandshurica Wood Using Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5521; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165521 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Supercritical carbon dioxide (ScCO2), known for such features as good solubility and mass transfer properties, can be an efficient drying medium for various materials, such as wood, by filling the pore space and dissolving water in the cell cavity without altering
[...] Read more.
Supercritical carbon dioxide (ScCO2), known for such features as good solubility and mass transfer properties, can be an efficient drying medium for various materials, such as wood, by filling the pore space and dissolving water in the cell cavity without altering the microstructure. In this study, two specimens of Juglans mandshurica wood with a length of 30 mm and 140 mm were subjected to ScCO2 dewatering under four different pressure and temperature conditions. The results showed that the drying rate is mainly influenced by pressure and temperature, with pressure having the more significant effect. Moreover, the efficiency of dewatering was not dependent on the sample length under the same conditions. The moisture content (MC) was the same along the longitudinal direction throughout both the surfaces and core of the wood. While there were no significant differences in dewatering rate between tangential and radial directions and lengths of samples, significant MC gradient differences were noted along wood in radial and tangential directions. During ScCO2 dewatering, the dominant water transfer occurred from the middle towards the end surfaces along the wood’s longitudinal directions. Furthermore, ScCO2 dewatering did not result in any shrinkage or significant drying stress, but it did cause some swelling in Juglans mandshurica wood.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Surface Modification and Applications of Wood Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
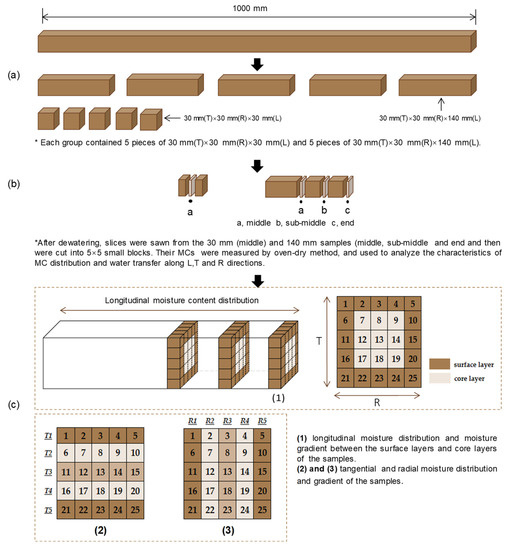
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Effect of Ultrafine Cement (UFC) on the Corrosion Resistance of Cement Soil in Peat Soil Environment
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5520; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165520 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Many peat soils are distributed around plateau lakes, and the reinforcement of peat soils with high organic matter content by ordinary cement cannot meet the actual engineering requirements. In order to obtain better mechanical properties and durability of the reinforcement, this experiment prepared
[...] Read more.
Many peat soils are distributed around plateau lakes, and the reinforcement of peat soils with high organic matter content by ordinary cement cannot meet the actual engineering requirements. In order to obtain better mechanical properties and durability of the reinforcement, this experiment prepared peat soil by mixing humic acid reagent into the alluvial clay soil with low organic matter content. The cement soil samples were prepared by adding cement and ultrafine cement (UFC) by stirring method; the samples were then soaked in fulvic acid solution to simulate the cement soil in the peat soil environment. Using the unconfined compressive strength (UCS) test, scanning electron microscope (SEM) test, and pores and cracks analysis system (PCAS) test, the effect of UFC content change on cement soil’s humic acid erosion resistance was explored, and the optimal UFC content range was sought. The results of the UCS test show that with an increase in immersion time, the strength curves of cement soil samples gradually increase to the peak strength and then decrease. Significant differences in the time correspond to the peak strength, and the overall presentation is two processes: the strength enhancement stage and the corrosion stage of the sample. The incorporation of UFC makes the cement soil in the peat soil environment exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, and the optimal UFC content is 10%. The results of the SEM and PCAS tests show that the microstructure of cement soil after immersion time exceeds 90 days, increases with an increase in immersion time, and its structural connectivity gradually weakens. The excellent characteristics of UFC particles, such as small particle size, narrow particle size distribution, fast hydration reaction rate, high hydration degree, and many hydration products, weakened the adverse effects of humic acid on the cement soil structure to a certain extent. Therefore, although the number of macropores increases, they are not connected. It still presents a relatively compact honeycomb overall structure, which correlates well with the UCS results.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Microstructural, Mechanical, and Durability Characteristics of Cementitious Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Re on the Plastic Hardening Mechanism of Alloyed Copper
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5519; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165519 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this paper, we investigated the effect of adding rhenium to Cu-Ni-Si alloys on the mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of these alloys. The scientific objective was to analyze the effect of Re addition on the microstructure of heat- and cold-treated CuNi2Si1 alloys.
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we investigated the effect of adding rhenium to Cu-Ni-Si alloys on the mechanical properties and electrical conductivity of these alloys. The scientific objective was to analyze the effect of Re addition on the microstructure of heat- and cold-treated CuNi2Si1 alloys. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM, STEM) and scanning electron microscopy (EDS, WDS) were used to examine the microstructure. Orientation mapping was also performed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) equipped with a backscattered electron diffraction (EBSD) system. In addition, hardness at low load and conductivity were tested. The obtained results showed that modifying the chemical composition of Re (0.6 wt%) inhibits the recrystallization process in the CuNi2Si1 alloy, which was cold deformed and then subjected to recrystallization annealing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Mechanics and Analysis of Advanced Materials and Structures - 2nd Volume)
►▼
Show Figures
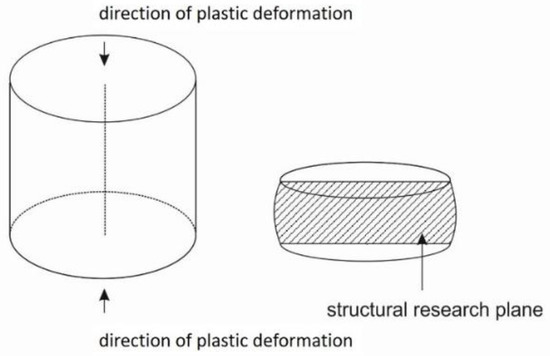
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Thermomechanical Properties of Neutron Irradiated Al3Hf-Al Thermal Neutron Absorber Materials
by
, , , , and
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5518; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165518 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
A thermal neutron absorber material composed of Al3Hf particles in an aluminum matrix is under development for the Advanced Test Reactor. This metal matrix composite was fabricated via hot pressing of high-purity aluminum and micrometer-size Al3Hf powders at volume
[...] Read more.
A thermal neutron absorber material composed of Al3Hf particles in an aluminum matrix is under development for the Advanced Test Reactor. This metal matrix composite was fabricated via hot pressing of high-purity aluminum and micrometer-size Al3Hf powders at volume fractions of 20.0, 28.4, and 36.5%. Room temperature tensile and hardness testing of unirradiated specimens revealed a linear relationship between volume fraction and strength, while the tensile data showed a strong decrease in elongation between the 20 and 36.5% volume fraction materials. Tensile tests conducted at 200 °C on unirradiated material revealed similar trends. Evaluations were then conducted on specimens irradiated at 66 to 75 °C to four dose levels ranging from approximately 1 to 4 dpa. Tensile properties exhibited the typical increase in strength and decrease in ductility with dose that are common for metallic materials irradiated at ≤0.4Tm. Hardness also increased with neutron dose. The difference in strength between the three different volume fraction materials was roughly constant as the dose increased. Nanoindentation measurements of Al3Hf particles in the 28.4 vol% material showed the expected trend of increased hardness with irradiation dose. Transmission electron microscopy revealed oxygen at the interface between the Al3Hf particles and aluminum matrix in the irradiated material. Scanning electron microscopy of the exterior surface of tensile tested specimens revealed that deformation of the material occurs via plastic deformation of the Al matrix, cracking of the Al3Hf particles, and to a lesser extent, tearing of the matrix away from the particles. The fracture surface of an irradiated 28.4 vol% specimen showed failure by brittle fracture in the particles and ductile tearing of the aluminum matrix with no loss of cohesion between the particles and matrix. The coefficient of thermal expansion decreased upon irradiation, with a maximum change of −6.3% for the annealed irradiated 36.5 vol% specimen.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Characterization Techniques on Nuclear Fuels and Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Design and Evaluation of Smart Textile Actuator with Chain Structure
by
and
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5517; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165517 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Textiles composed of fibers can have their mechanical properties adjusted by changing the arrangement of the fibers, such as strength and flexibility. Particularly, in the case of smart textiles incorporating active materials, various deformations could be created based on fiber patterns that determine
[...] Read more.
Textiles composed of fibers can have their mechanical properties adjusted by changing the arrangement of the fibers, such as strength and flexibility. Particularly, in the case of smart textiles incorporating active materials, various deformations could be created based on fiber patterns that determine the directivity of active materials. In this study, we design a smart fiber-based textile actuator with a chain structure and evaluate its actuation characteristics. Smart fiber composed of shape memory alloy (SMA) generates deformation when the electric current is applied, causing the phase transformation of SMA. We fabricated the smart chain column and evaluated its actuating mechanism based on the size of the chain and the number of rows. In addition, a crochet textile actuator was designed using interlooping smart chains and developed into a soft gripper that can grab objects. With experimental verifications, this study provides an investigation of the relationship between the chain actuator’s deformation, actuating force, actuator temperature, and strain. The results of this study are expected to be relevant to textile applications, wearable devices, and other technical fields that require coordination with the human body. Additionally, it is expected that it can be utilized to configure a system capable of flexible operation by combining rigid elements such as batteries and sensors with textiles.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Design, Characterization and Novel Applications of Shape Memory Alloys)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Use of Biosilica to Increase the Compressive Strength of Cement Mortar: The Effect of the Mixing Method
by
, , , , , , and
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5516; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165516 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this work, the effect of biosilica concentration and two different mixing methods with Portland cement on the compressive strength of cement-based mortars were investigated. The following values of the biosilica concentration of cement weight were investigated։ 2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10 wt.%.
[...] Read more.
In this work, the effect of biosilica concentration and two different mixing methods with Portland cement on the compressive strength of cement-based mortars were investigated. The following values of the biosilica concentration of cement weight were investigated։ 2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10 wt.%. The mortar was prepared using the following two biosilica mixing methods: First, biosilica was mixed with cement and appropriate samples were prepared. For the other mixing method, samples were prepared by dissolving biosilica in water using a magnetic stirrer. Compressive tests were carried out on an automatic compression machine with a loading rate of 2.4 kN/s at the age of 7 and 28 days. It is shown that, for all cases, the compressive strength has the maximum value of 10% biosilica concentration. In particular, in the case of the first mixing method, the compressive strength of the specimen over 7 days of curing increased by 30.5%, and by 36.5% for a curing period of 28 days. In the case of the second mixing method, the compressive strength of the specimen over 7 days of curing increased by 23.4%, and by 47.3% for a curing period of 28 days. Additionally, using the first and second mixing methods, the water absorption parameters were reduced by 22% and 34%, respectively. Finally, it is worth noting that the obtained results were intend to provide valuable insights into optimizing biosilica incorporation in cement mortar. With the aim of contributing to the advancement of construction materials, this research delves into the intriguing application of biosilica in cement mortar, emphasizing the significant impact of mixing techniques on the resultant compressive strength.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recycled Materials in Civil Engineering Application)
►▼
Show Figures
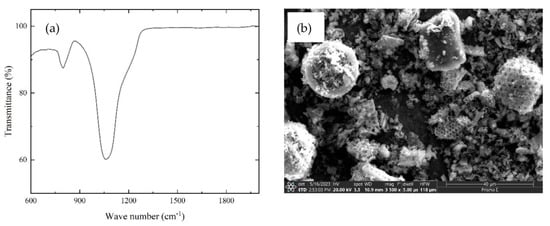
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Plastic Roads in Asia: Current Implementations and Should It Be Considered?
by
, , , , , , , and
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5515; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165515 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The rapid economic and industrial growth experienced in the Asian region has significantly increased waste production, particularly single-use plastic. This surge in waste poses a significant challenge for these countries’ municipal solid waste management systems. Consequently, there is a pressing need for progressive
[...] Read more.
The rapid economic and industrial growth experienced in the Asian region has significantly increased waste production, particularly single-use plastic. This surge in waste poses a significant challenge for these countries’ municipal solid waste management systems. Consequently, there is a pressing need for progressive and effective solutions to address the plastic waste issue. One promising initiative involves utilizing used plastic to produce components for asphalt pavement. The concept of plastic road technology has gained traction in Asia, with 32 countries displaying varying levels of interest, ranging from small-scale laboratory experiments to large-scale construction projects. However, as a relatively new technology, plastic road implementation requires continuous and comprehensive environmental and health risk assessments to ascertain its viability as a reliable green technology. This review paper presents the current findings and potential implementation of plastic-modified asphalt in Asian countries, with particular attention given to its environmental and human health impacts. While plastic asphalt roads hold promise in waste reduction, improved asphalt properties, and cost savings, it is imperative to thoroughly consider the environmental and health impacts, quality control measures, recycling limitations, and long-term performance of this road construction material. Further research and evaluation are needed to fully understand the viability and sustainability of plastic asphalt roads. This will enable a comprehensive assessment of its potential benefits and drawbacks, aiding in developing robust guidelines and standards for its implementation. By addressing these considerations, it will be possible to optimize the utilization of plastic waste in road construction and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Apple-like Shape of Freezing Paraffin Wax Droplets and Its Origin
by
, , , , and
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5514; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165514 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Paraffin wax stores energy in the form of latent heat at a nearly constant temperature during melting and releases this energy during solidification. This effect is used in industrial energy storage. At the same time, the possible deformation of even small volumes of
[...] Read more.
Paraffin wax stores energy in the form of latent heat at a nearly constant temperature during melting and releases this energy during solidification. This effect is used in industrial energy storage. At the same time, the possible deformation of even small volumes of material as a result of phase change is insufficiently studied. In this paper, the physical nature of such deformation, probably for the first time, is studied on the example of a droplet of paraffin wax. An unusual change in the shape of a melted droplet of paraffin wax placed on a relatively cold glass plate was observed in the laboratory experiments. As the droplet solidifies, its upper surface becomes nearly flat, and a dimple is formed in the center of this surface, making the droplet look like a fruit (pumpkins are more commonly shaped like this, but the authors prefer apples). A series of experiments, as well as physical and numerical modeling of the droplet’s thermal state, taking into account the formation of a mushy zone between liquidus and solidus, made it possible to understand the role of gravity and gradual increase in viscosity and density of paraffin wax on changing the droplet shape and, in particular, to clarify the mechanism of formation of the dimple on its upper. It was shown that the mushy zone between the liquidus and solidus of the paraffin wax is responsible for the dimple formation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Phase Change Materials and Storage Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
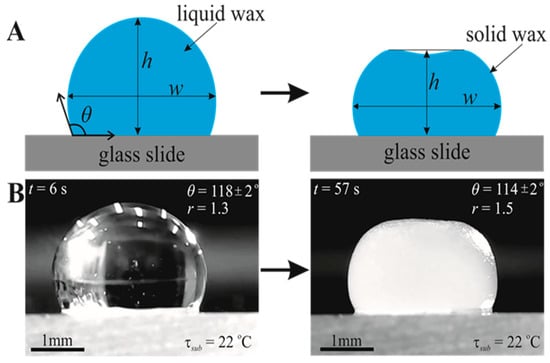
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Properties of Self-Compacting Concrete Produced with Optimized Volumes of Calcined Clay and Rice Husk Ash—Emphasis on Rheology, Flowability Retention and Durability
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5513; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165513 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The durability of concrete requires a dense microstructure which can be achieved by using self-compacting concrete (SCC). Both calcined clay (CC) and rice husk ash (RHA) are promising supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) that can partially replace cement, but their use in SCC is
[...] Read more.
The durability of concrete requires a dense microstructure which can be achieved by using self-compacting concrete (SCC). Both calcined clay (CC) and rice husk ash (RHA) are promising supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) that can partially replace cement, but their use in SCC is critical due to their higher water demand (WD) and specific surface area (SSA) compared to cement. The effect of partial substitution of cement at 20 vol-% with binary and ternary blends of CC and RHA on flowability retention and durability of SCC was investigated. The empirical method of SCC design was adopted considering the physical properties of both CC and RHA. The deformability of the SCC was evaluated using the slump flow and J-ring tests. The T500 time and the V-funnel test were used to assess the viscosity of the SCC. The flowability retention was monitored by the plunger method, and flow resistance was determined based on the rheological measurements of SCC. The evolution of the hydrate phases of the binder in SCC was determined by thermogravimetric analysis, while the durability was evaluated by a rapid chloride migration test. Cement partial replacement with 20 vol-% CC has no significant effect on fresh SCC, flowability retention, compressive strength and durability properties. On the other hand, 20 vol-% RHA requires a higher dosage of SP to achieve self-compactability and increase the viscosity of SCC. Its flowability retention is only up to 30 min after mixing and exhibited higher flow resistance. It consumes more calcium hydroxide (CH) and improves the compressive strength and chloride resistance of SCC. The ternary blending with CC and RHA yielded better fresh SCC properties compared to the binary blend with RHA, while an improved chloride penetration resistance could be achieved compared to the binary CC blend.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The 15th Anniversary of Materials—Recent Advances in Construction and Building Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
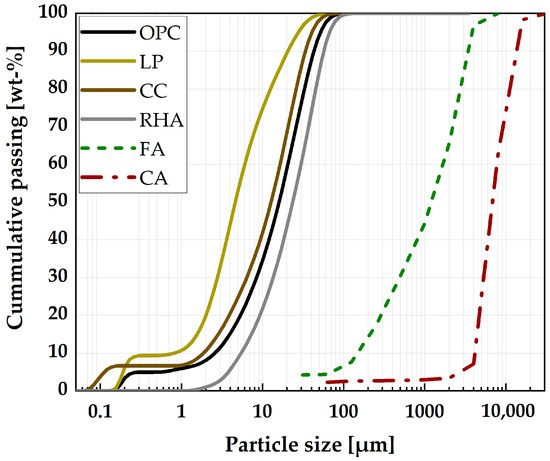
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Nitrogen Oxide Reduction Performance in Permeable Concrete Surfaces Treated with a TiO2 Photocatalyst
by
and
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5512; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165512 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Fine dust, recently classified as a carcinogen, has raised concerns about the health effects of air pollution. Vehicle emissions, particularly nitrogen oxide (NOx), contribute to ultrafine dust formation as a fine dust precursor. A photocatalyst, such as titanium dioxide (TiO2
[...] Read more.
Fine dust, recently classified as a carcinogen, has raised concerns about the health effects of air pollution. Vehicle emissions, particularly nitrogen oxide (NOx), contribute to ultrafine dust formation as a fine dust precursor. A photocatalyst, such as titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a material that causes a catalytic reaction when exposed to light, has exceptional characteristics such as decomposition of pollutants, and can be used permanently. This study aimed to investigate NOx reduction performance by developing ecofriendly permeable concrete with photocatalytic treatment to reduce fine dust generated from road mobile pollution sources. Permeable concrete specimens containing an activated loess and zeolite admixture were prepared and subjected to mechanical and durability tests. All specimens, including the control (CTRL) and admixture, met quality standard SPS-F-KSPIC-001-2006 for road pavement. Slip resistance and permeability coefficient also satisfied the standards, while freeze–thaw evaluation criteria were met only by CTRL and A1Z1 specimens. NOx reduction performance of the permeable concrete treated with TiO2 photocatalyst was assessed using ISO standard and tank chambers. NOx reduction efficiency of up to 77.5% was confirmed in the permeable concrete specimen with TiO2 content of 7.5%. Nitrate concentration measurements indirectly confirmed photolysis of nitrogen oxide. Incorporating TiO2 in construction materials such as roads and sidewalks can improve the atmospheric environment for pedestrians near roads by reducing NOx levels through photocatalysis.
Full article
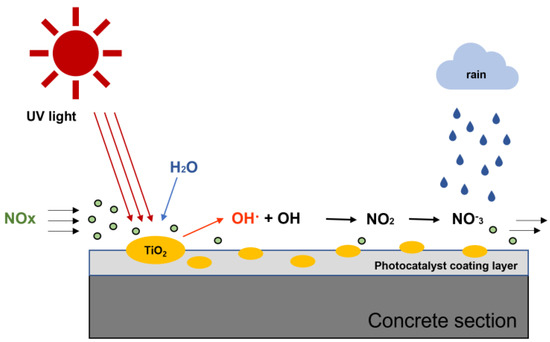
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Study of Electroless-Deposited Zn on the Surface of Mg-Li Alloy
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5511; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165511 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The Mg-Li alloy stands as the lightest metallic structural material known to date, finding a wide range of applications. However, its development has been hindered by its susceptibility to oxidation and corrosion. In this study, we aimed to address this issue by employing
[...] Read more.
The Mg-Li alloy stands as the lightest metallic structural material known to date, finding a wide range of applications. However, its development has been hindered by its susceptibility to oxidation and corrosion. In this study, we aimed to address this issue by employing electroless deposition to form a protective zinc layer on the surface of a magnesium–lithium alloy. The optimization of the zinc layer was achieved through varying parameters such as the zinc dipping time (1~10 min), temperature (20~70 °C), and zinc content (20~200 g/L). Surface characterization was performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction, while electrochemical tests and scratch tests were conducted to evaluate corrosion resistance and coating adhesion. The results demonstrated the successful formation of a uniform and dense pure zinc layer on the surface of the Mg-Li alloy when the zinc-dipping time was set at 5 min, the temperature was at 30 °C, and the zinc content was at 50 g/L. Under these conditions, the corrosion potential of the Mg-Li alloy experienced the greatest positive shift, reaching as high as −1.38 V. Additionally, the corrosion current was minimized, measuring at 2.78 × 10−6 A/cm2. Furthermore, the maximum arc tolerance radius was observed. Consequently, the electroless deposition of zinc onto Mg-Li alloys significantly improves their corrosion resistance and bonding, opening up new prospects for the application of zinc-plated Mg-Li alloys.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Metals and Alloys)
►▼
Show Figures
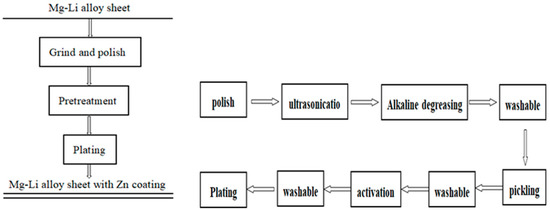
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Microstructure of TiAl Capsules Processed by Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion Followed by Post-Hot Isostatic Pressing
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5510; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165510 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The microstructures of intermetallic γ-titanium aluminide (TiAl) alloys are subjected to a certain degree of Al evaporation when processed by electron beam powder bed fusion (EB-PBF). The magnitude of the Al-loss is mainly correlated with the process parameters, and highly energetic parameters produce
[...] Read more.
The microstructures of intermetallic γ-titanium aluminide (TiAl) alloys are subjected to a certain degree of Al evaporation when processed by electron beam powder bed fusion (EB-PBF). The magnitude of the Al-loss is mainly correlated with the process parameters, and highly energetic parameters produce significant Al evaporation. The Al-loss leads to different microstructures, including the formation of inhomogeneous banded structures, thus negatively affecting its mechanical performance. For this reason, the current work deals with creating EB-PBFed TiAl capsules with the inner part produced using only the pre-heating step and melting parameters with low energetic parameters applying high beam speed from 5000 to 3000 mm/s. This approach is investigated to reduce the Al-loss and microstructure inhomogeneity after hot isostatic pressing (HIP). The results showed that the HIP treatment effectively densified the capsules obtaining a relative density of around 100%. After HIP, the capsules produced with the inner part melted at 3000 mm/s presented a lower area shrinkage (around 6.6%) compared to the capsules produced using only the pre-heating step in the core part (around 20.7%). The different magnitudes of shrinkage derived from different levels of residual porosity consolidated during the HIP process. The HIPed capsules exhibited the presence of previous particle boundaries (PPBs), covered by α2 phases. Notably, applying low energetic parameters to melt the core partially eliminates the particles’ surface, thus reducing the PPBs formation. In this case, the capsules melted with low energetic parameters (3000 mm/s) exhibited α2 concentration of 3.5% and an average size of 13 µm compared to the capsules produced with the pre-heating step in the inner part with an α2 around 5.7% and an average size around 23 µm. Moreover, the Al-loss of the capsules was drastically limited, as determined by X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis. More in detail, the capsules produced with the pre-heating step reported an atomic percentage of Al of 48.75, while using low energetic melting parameters led to 48.36. This result was interesting, considering that the massive samples produced with standard parameters (so more energetic ones) revealed atomic Al percentage from 48.04 to 47.70. Finally, the recycled small particles showed a higher fraction of α2 phases with respect to the coarse particles, as determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Application of Powder Metallurgy Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of Liposomal and Liquid Crystalline Lipidic Nanoparticles with Non-Ionic Surfactants for Quercetin Incorporation
by
, , , , , , and
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5509; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165509 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The aim of the present study is the development, physicochemical characterization, and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of both empty and quercetin-loaded HSPC (hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine) liposomes, GMO (glyceryl monooleate) liquid crystalline nanoparticles, and PHYT (phytantriol) liquid crystalline nanoparticles. Specifically, HSPC phospholipids were mixed
[...] Read more.
The aim of the present study is the development, physicochemical characterization, and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of both empty and quercetin-loaded HSPC (hydrogenated soy phosphatidylcholine) liposomes, GMO (glyceryl monooleate) liquid crystalline nanoparticles, and PHYT (phytantriol) liquid crystalline nanoparticles. Specifically, HSPC phospholipids were mixed with different non-ionic surfactant molecules (Tween 80 and/or Span 80) for liposomal formulations, whereas both GMO and PHYT lipids were mixed with Span 80 and Tween 80 as alternative stabilizers, as well as with Poloxamer P407 in different ratios for liquid crystalline formulations. Subsequently, their physicochemical properties, such as size, size distribution, and ζ-potential were assessed by the dynamic and electrophoretic light scattering (DLS/ELS) techniques in both aqueous and biological medium with serum proteins. The in vitro biological evaluation of the empty nanosystems was performed by using the MTT cell viability and proliferation assay. Finally, the entrapment efficiency of quercetin was calculated and the differences between the two different categories of lipidic nanoparticles were highlighted. According to the results, the incorporation of the non-ionic surfactants yields a successful stabilization and physicochemical stability of both liposomal and liquid crystalline nanoparticles. Moreover, in combination with an appropriate biosafety in vitro profile, increased encapsulation efficiency of quercetin was achieved. Overall, the addition of surfactants improved the nanosystem’s stealth properties. In conclusion, the results indicate that the physicochemical properties were strictly affected by the formulation parameters, such as the type of surfactant.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Drug Delivery: Recent Developments and Future Prospects (Volume II))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Origin and Evolution of Cracks in the Glaze Surface of a Ceramic during the Cooling Process
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5508; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165508 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Because of the significant difference between the thermal expansion coefficients of ceramic blank and glaze, the glaze typically undergoes more pronounced shrinkage than the blank during ceramic cooling, which results in high stress concentrations and cracking. In this study, the mechanical mechanism of
[...] Read more.
Because of the significant difference between the thermal expansion coefficients of ceramic blank and glaze, the glaze typically undergoes more pronounced shrinkage than the blank during ceramic cooling, which results in high stress concentrations and cracking. In this study, the mechanical mechanism of glaze cracking is studied, based on the statistical strength theory, damage mechanics, and continuum mechanics. Furthermore, the influence of the glaze layer thickness, heat transfer coefficient, expansion coefficient, and temperature difference on the creation and propagation of inner microcracks is systematically investigated, and the final discrete fracture network of ceramics is discussed at the specific crack saturation state. The results show that (1) a higher heat transfer coefficient will lead to a more uniform distribution of the surface temperature and a faster cooling process of the ceramics, reducing the number of microcracks when the ambient temperature is reached; (2) the thinner glaze layer is less prone to cracking when its thickness is smaller than that of the blank. However, when the thickness of the glaze layer is similar to that of the blank, the increased thickness of the glaze layer will increase the number of cracks on its surface; and (3) when the expansion coefficient of the glaze layer is smaller than that of the blank, cracks will not occur inside the glaze layer. However, as the coefficient of the thermal expansion of the glaze layer continuously rises, the number of cracks on its surface will first increase and then decrease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Damage, Fracture and Fatigue of Ceramic Matrix Composites (CMCs))
►▼
Show Figures
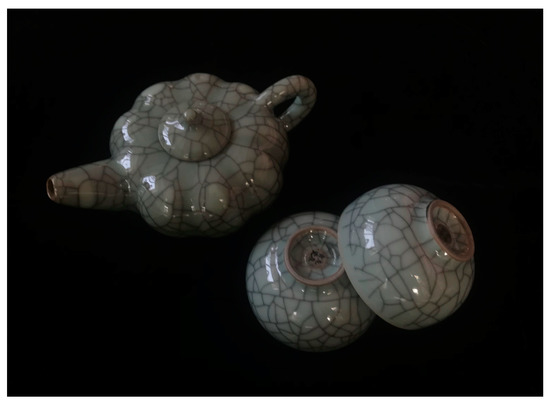

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Influence of 3D Printing Core Construction (Binder Jetting) on the Amount of Generated Gases in the Environmental and Technological Aspect
by
, , , , , and
Materials 2023, 16(16), 5507; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16165507 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
This article presents the findings of a study focusing on the gas generation of 3D-printed cores fabricated using binder-jetting technology with furfuryl resin. The research aimed to compare gas emission levels, where the volume generated during the thermal degradation of the binder significantly
[...] Read more.
This article presents the findings of a study focusing on the gas generation of 3D-printed cores fabricated using binder-jetting technology with furfuryl resin. The research aimed to compare gas emission levels, where the volume generated during the thermal degradation of the binder significantly impacts the propensity for gaseous defects in foundries. The study also investigated the influence of the binder type (conventional vs. 3D-printed dedicated binder) and core construction (shell core) on the quantity of gaseous products from the BTEX group formed during the pouring of liquid foundry metal into the cores. The results revealed that the emitted gas volume during the thermal decomposition of the organic binder depended on the core sand components and binder type. Cores produced using conventional methods emitted the least gases due to lower binder content. Increasing Kaltharz U404 resin to 1.5 parts by weight resulted in a 37% rise in gas volume and 27% higher benzene emission. Adopting shell cores reduced gas volume by over 20% (retaining sand with hardener) and 30% (removing sand with hardener), presenting an eco-friendly solution with reduced benzene emissions and core production costs. Shell cores facilitated the quicker removal of gaseous binder decomposition products, reducing the likelihood of casting defects. The disparity in benzene emissions between 3D-printed and vibratory-mixed solid cores is attributed to the sample preparation process, wherein 3D printing ensured greater uniformity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research and Development in the World Foundry Engineering: Materials, Properties and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
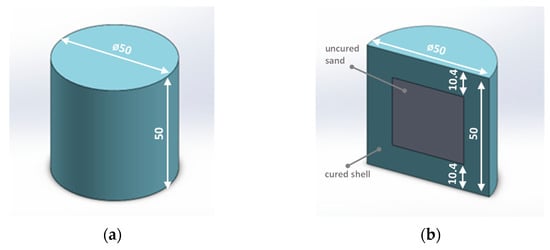
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Materials Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Chemistry, Compounds, Crystals, Materials, Molecules
Advanced Structural Crystals
Topic Editors: Małgorzata Hołyńska, Ionut TrancaDeadline: 31 August 2023
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Coatings, JMMP, Materials, Metals
Welding and Joining of Materials in Off-shore and Energy Industry
Topic Editors: Dariusz Fydrych, Jacek Tomków, Aleksandra Świerczyńska, Grzegorz Rogalski, Sergey G. Parshin, Chandan Pandey, Michał Landowski, Hamed Aghajani Derazkola, Thomas HasselDeadline: 15 September 2023
Topic in
Batteries, Designs, Energies, Materials, Sustainability
Materials for Energy Harvesting and Storage
Topic Editors: Xia Lu, Xueyi LuDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Buildings, Infrastructures, Materials, Polymers, Sustainability
Materials for Carbon-Neutral Infrastructures
Topic Editors: Yue Xiao, Denis Jelagin, Dae-Wook Park, Zongwu ChenDeadline: 20 October 2023

Conferences
27 October–10 November 2023
The 4th International Electronic Conference on Applied Sciences (ASEC2023)

Special Issues
Special Issue in
Materials
Application of Scanning Probe Techniques in the Study of Biomaterials and Biomechanisms
Guest Editors: Claudio Canale, Ornella CavalleriDeadline: 10 August 2023
Special Issue in
Materials
Functional Carbon-Based Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites
Guest Editors: Hyungwoo Kim, Doojin Lee, Won Seok ChiDeadline: 20 August 2023
Special Issue in
Materials
Interplay between Dental Biomaterials and Intraoral Environment: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Guest Editors: Edoardo Staderini, Patrizia Gallenzi, Michele TepedinoDeadline: 31 August 2023
Special Issue in
Materials
Nanostructured Materials for Electrochemical Energy Storage
Guest Editors: Christian M. Julien, Boris MarkovskyDeadline: 10 September 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Materials
Advanced Biomaterials for Cells Adhesion, Proliferation and Differentiation
Collection Editor: Guoping Chen
Topical Collection in
Materials
Catalysts: Preparation, Catalytic Performance and Catalytic Reaction
Collection Editors: Gina Pecchi, Cristian H. Campos