Journal Description
Sustainability
Sustainability
is an international, cross-disciplinary, scholarly, peer-reviewed and open access journal of environmental, cultural, economic, and social sustainability of human beings. It provides an advanced forum for studies related to sustainability and sustainable development, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Canadian Urban Transit Research & Innovation Consortium (CUTRIC) and International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction (CIB) are affiliated with Sustainability and their members receive discounts of the article processing charge.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), GEOBASE, GeoRef, Inspec, AGRIS, RePEc, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Environmental Studies) / CiteScore - Q1 (Geography, Planning and Development)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 18.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Sustainability.
- Companion journals for Sustainability include: World, Sustainable Chemistry, Conservation, Future Transportation, Architecture, Standards, Merits and Wind.
Impact Factor:
3.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.0 (2022)
Latest Articles
Dynamic Incentive Contract of Government for Port Enterprises to Reduce Emissions in the Blockchain Era: Considering Carbon Trading Policy
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12148; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612148 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Blockchain technology is very useful. This paper considers the application of blockchain technology to smart contracts, green certification, and market information disclosure, and introduces the carbon trading market price as a parameter to solve the dynamic incentive problem of the government for port
[...] Read more.
Blockchain technology is very useful. This paper considers the application of blockchain technology to smart contracts, green certification, and market information disclosure, and introduces the carbon trading market price as a parameter to solve the dynamic incentive problem of the government for port enterprises to reduce emissions under the carbon trading policy. Based on the state change of port carbon emission reduction, this paper uses principal–agent theory to construct the dynamic incentive contract model of government without blockchain, with blockchain, and when carbon trading is considered under blockchain, respectively, and uses the optimal control method to solve and analyze the model. This paper finds that only when the opportunity cost of port enterprises is greater than a certain critical point and the fixed cost of blockchain is less than a certain critical point, the implementation of blockchain will help improve government efficiency. However, only when the critical value of carbon emission reduction of port enterprises and the unit operating cost of blockchain are small, the government should start the carbon trading market under blockchain technology. Through numerical simulation, this paper also finds that it is usually beneficial for the government to regulate and appropriately increase the carbon trading market price.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Transition in Green Maritime Transportation and Port Management)
Open AccessArticle
Factors Affecting the Implementation of Online Food Delivery and Its Impact on Restaurant Performance during the COVID-19 Pandemic
by
and
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12147; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612147 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many restaurants implemented online food delivery (OFD) platforms to serve customers. However, it remains unclear how restaurant managers decide to implement OFD and whether or not the implementation can improve performance. We view OFD implementation as a form of
[...] Read more.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, many restaurants implemented online food delivery (OFD) platforms to serve customers. However, it remains unclear how restaurant managers decide to implement OFD and whether or not the implementation can improve performance. We view OFD implementation as a form of service innovation. This study investigates and explains the reasons why restaurants implemented an OFD platform during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the impact of that implementation on restaurant performance, based on service innovation theory. An internet survey was conducted to collect data from restaurant owners or managers to test the proposed research model. The results show that the perceived benefit of increasing the firm’s reach is the key driver of OFD implementation, and the implementation has a positive impact on both financial and non-financial performance. A follow-up interview was also conducted to obtain the opinions of industry experts, who explained the phenomena. The research findings can advance our understanding of how restaurant managers decide to innovate by implementing OFD services and help them better understand whether and how the implementation of this service can actually improve performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable E-commerce and Online Marketing Research)
Open AccessArticle
Analyzing Driving Safety on Prairie Highways: A Study of Drivers’ Visual Search Behavior in Varying Traffic Environments
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12146; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612146 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
This study aimed to investigate disparities in drivers’ visual search behavior across various typical traffic conditions on prairie highways and analyze driving safety at the visual search level. The study captured eye movement data from drivers across six real-world traffic environments: free driving,
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to investigate disparities in drivers’ visual search behavior across various typical traffic conditions on prairie highways and analyze driving safety at the visual search level. The study captured eye movement data from drivers across six real-world traffic environments: free driving, vehicle-following, oncoming vehicles, rear vehicles overtaking cut-in, roadside risks, and driving through intersections, by carrying out a real vehicle test on a prairie highway. The drivers’ visual search area was divided into five areas using clustering principles. By integrating the Markov chain and information entropy theory, the information entropy of fixation distribution (IEFD) was constructed to quantify the complexity of drivers’ traffic information search. Additionally, the main area of visual search (MAVS) and the peak-to-average ratio of saccade velocity (PARSV) were introduced to measure visual search range and stability, respectively. The study culminated in the creation of a visual search load evaluation model that utilizes both VIKOR and improved CRITIC methodologies. The findings indicated that while drivers’ visual distribution and transfer modes vary across different prairie highway traffic environments, the current lane consistently remained their primary area of search for traffic information. Furthermore, it was found that each visual search indicator displayed significant statistical differences as traffic environments changed. Particularly when encountering roadside risks, drivers’ visual search load increased significantly, leading to a considerable decrease in driving safety.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Technology, User Behavior and Infrastructure for Sustainable Traffic Safety)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Antecedents of Collaborative Behavior for Climate Change Mitigation among South Koreans: The Moderation Analyses of a Sense of Community as Responsibility, Neighborliness, and Trust
by
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12145; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612145 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The collective efforts of various social actors from different sectors have contributed to climate change mitigation. Identifying the important antecedents of collaborative behavior to address climate change helps us understand the underlying process. This study focused on important theoretical frameworks that determine collaborative
[...] Read more.
The collective efforts of various social actors from different sectors have contributed to climate change mitigation. Identifying the important antecedents of collaborative behavior to address climate change helps us understand the underlying process. This study focused on important theoretical frameworks that determine collaborative behavior as civic engagement. Specifically, the study examines perceived societal risk to future generations, sense of community as responsibility (SOC-R), neighborliness, and trust in collaborative behavior to mitigate climate change. It also investigates the boundary conditions of the effects of societal risk perception on collaborative behavior change by examining the moderating roles of SOC-R, neighborliness, and trust. A nationwide online survey was conducted in South Korea. The findings reveal significant effects of societal risk perception and SOC-R on behavioral intention. Moreover, SOC-R and trust moderated the causal relationship between societal risk perception and behavioral intention, such that the relationship was more pronounced at lower SOC-R and trust. These findings have implications for communication practices and policy making that motivate collective action against climate change in South Korea.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Environmental Behavior and Climate Change)
Open AccessArticle
Reconfiguring Farming Systems of Smallholders with Market-Led Approach: A Case Study in Northeast Thailand
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12144; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612144 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Agricultural research and development organizations are under pressure to shift from increasing productivity of crops to increasing the profitability and competitiveness of smallholders and linking small-scale farmers to profitable markets. This paper discusses the efforts to assist small-scale farmers to become more sustainable
[...] Read more.
Agricultural research and development organizations are under pressure to shift from increasing productivity of crops to increasing the profitability and competitiveness of smallholders and linking small-scale farmers to profitable markets. This paper discusses the efforts to assist small-scale farmers to become more sustainable and market oriented. Data were taken from a 5-year participatory action project in a village in Northeast Thailand during 2014–2018. We found that a market-led extension approach can enable farmers to optimize their returns from farming by selecting farm enterprises based on market opportunities for both existing and new products. Farmers need to apply post-harvesting management, including processing, grading, standardization of produce, value adding, packaging, branding, and certification in the process. Collaboration and long-term commitments on the part of scientists, local stakeholders, policymakers, and funding organizations need to be furthered strengthened.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Urban and Rural Development)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Quantifying the Impacts of Urbanization on Urban Agriculture and Food Security in the Megacity Lahore, Pakistan
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12143; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612143 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
As a response to food security, urban agriculture is essential for sustainable development. The primary goal of this study is to provide the basic formulation and theoretical knowledge for sustainable urban agriculture by analyzing the impact of urbanization on urban agriculture and food
[...] Read more.
As a response to food security, urban agriculture is essential for sustainable development. The primary goal of this study is to provide the basic formulation and theoretical knowledge for sustainable urban agriculture by analyzing the impact of urbanization on urban agriculture and food security. For the food security assessment, the variables included food consumption and quality of food as the independent variables, and monthly income of local dwellers as the dependent variable; these were considered for the regression analysis and statistical analysis. The food security assessment was checked and expressed using regression values of R, which was 0.857, and an adjusted R square, with a value of 0.728. The results show extensive change in food security issues and land use due to urbanization causes, large-scale damage to agricultural land in the area, and loss of biodiversity, which threaten food security by converting natural land into built-up areas. The study concludes that urban agriculture is a fundamental environmental activity to ensure food security by increasing food production for locals and improving urban biodiversity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security)
►▼
Show Figures
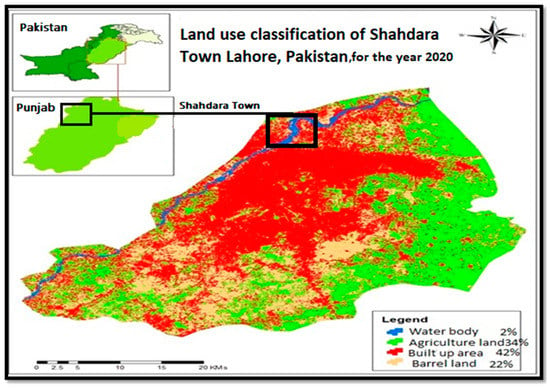
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
More Accurate Climate Trend Attribution by Using Cointegrating Vector Time Series Models
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12142; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612142 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Adapting to human-induced climate change is becoming an increasingly important aspect of sustainable development. To be able to do this effectively, it is important to know how much human influence has contributed to observed climate trends. Climate detection and attribution (D&A) studies achieve
[...] Read more.
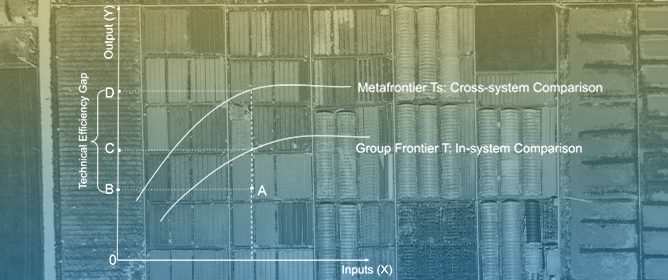
Adapting to human-induced climate change is becoming an increasingly important aspect of sustainable development. To be able to do this effectively, it is important to know how much human influence has contributed to observed climate trends. Climate detection and attribution (D&A) studies achieve this by estimating scaling factors usually obtained by performing a least squares regression of the observed trending climate variable on the equivalent variable simulated by a climate model. This study proposed instead to estimate scaling factors by using the econometric approach of dynamically modelling the time series as a cointegrating Vector Auto-Regressive (VAR) time series process. It is shown that a 2nd-order cointegrating VAR(2) model is theoretically justified if the observed and simulated variables can be represented as a one-box AR(1) response to a common integrated forcing. The VAR(2) model can be expressed as a Vector Error-Correction Model (VECM) and then fitted to the data to obtain the cointegration relationship, the stationary linear combination of the two variables, from which the scaling factor is then easily obtained. Estimates of the scaling factor from the VAR(2) model are critically compared to those from Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) and Total Least Squares (TLS) for annual Global Mean Surface Temperature (GMST) data simulated by a simple stochastic model of the carbon–climate system and for historical simulations from 16 climate models in the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project 5 (CMIP5) experiment. Results from the toy model simulations show that the slope estimates from OLS are negatively biased, TLS estimates are less biased but have high variance, and the VAR(2) estimates are unbiased and have lower variance and provide the most accurate estimates with smallest mean squared error. Similar behaviour is noted in the CMIP5 data. Hypothesis tests on the VAR(2) fits found strong evidence of a cointegrating relationship with the observations for all the CMIP5 simulations.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Statistics and Econometrics of Environment and Climate Change)
►▼
Show Figures
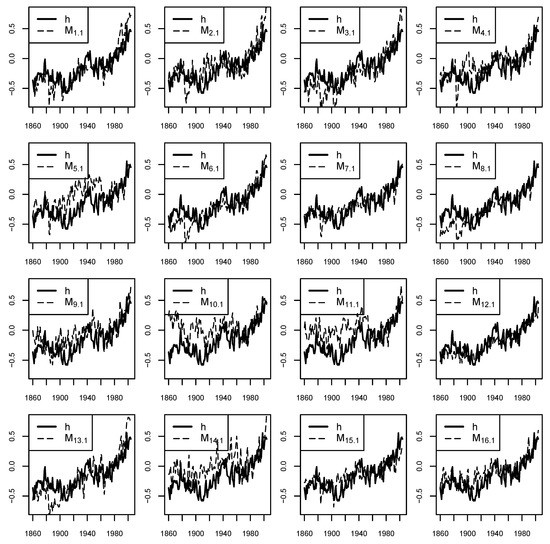
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Spatial Heterogeneity of Urban Road Network Fractal Characteristics and Influencing Factors
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12141; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612141 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Fractal geometry has provided a new perspective for urban road network morphology research. This study systematically verifies and analyzes the spatial heterogeneity of fractal characteristics and influencing factors of urban road networks using spatial analysis. Here, Tokyo Metropolis was selected as a case,
[...] Read more.
Fractal geometry has provided a new perspective for urban road network morphology research. This study systematically verifies and analyzes the spatial heterogeneity of fractal characteristics and influencing factors of urban road networks using spatial analysis. Here, Tokyo Metropolis was selected as a case, and the fractal dimensions of road networks were calculated. To determine the spatial heterogeneity in the relationship between fractal dimensions and influencing factors, we examined the spatial distribution characteristics of fractal dimensions using spatial autocorrelation analysis, selected population, build-up area density, and road network density as the explanatory variables, and established the global regression model and local regression model using ordinary least squares (OLS) and geographically weighted regression (GWR), respectively. The results indicated that the spatial distribution of fractal dimensions of the urban road network exhibited an obvious tendency toward geographical dependency. Considering the spatial heterogeneity in the relationship between the fractal characteristics of the road network and the influencing factors not only improves the reliability of analysis but also helps planners and decision-makers grasp the morphological characteristics of the urban road network and estimate the evolution of the road network, thereby promoting the development of urban road networks in a more orderly, efficient, and sustainable direction.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Transportation)
►▼
Show Figures
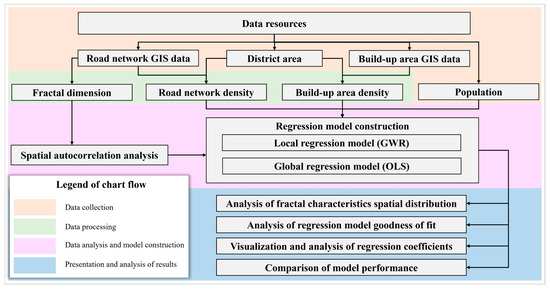
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Occupational Safety Courses Given in Undergraduate Departments in Turkey and Investigation of the Effect on Working Life
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12140; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612140 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this study, using the general survey model, which is one of the quantitative research methods, the evaluation of the occupational safety courses given in undergraduate departments in Turkey and their effects on working life were examined for 440 people who received their
[...] Read more.
In this study, using the general survey model, which is one of the quantitative research methods, the evaluation of the occupational safety courses given in undergraduate departments in Turkey and their effects on working life were examined for 440 people who received their undergraduate education and started their working life. An appropriate sampling method was preferred in the sample selection of the study. According to the research, the effect of occupational health and safety courses on working life, the contribution of occupational health and safety education, and occupational health and safety education’s contribution to awareness show significant differences according to age, gender, department, and work experience. When the relationship between them is examined, these relationships are positive and moderate. The results and survey average scores show that the theoretical courses on occupational health and safety in undergraduate programs of universities in Turkey are insufficient and should be supported by practice and training in working life.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Sustainable Education and Approaches)
Open AccessArticle
A Readiness Model and Factors Influencing Blockchain Adoption in Malaysia’s Software Sector: A Survey Study
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12139; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612139 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The technology of Blockchain may open up new potential for innovation and distinction. It can enable the software sector to develop more safe and transparent systems that can function in an environment without trust. The adoption rate still needs to be higher despite
[...] Read more.
The technology of Blockchain may open up new potential for innovation and distinction. It can enable the software sector to develop more safe and transparent systems that can function in an environment without trust. The adoption rate still needs to be higher despite the potential advantages; the relatively low adoption rate may be attributable to issues such as a lack of awareness, the difficulty of adoption, and ambiguity surrounding legal and regulatory frameworks. Considering technical, organizational, and environmental aspects, this study aims to determine the primary factors impacting the readiness of software firms to adopt Blockchain technology. The research on adopting Blockchain technology in the Malaysian software sector is limited. Using a quantitative method, the researchers used structural equation modeling to analyze 251 survey responses from the Malaysian software sector. In light of the findings, eight hypotheses were considered significant, and one hypothesis was rejected. At the same time, the R2 indicated that all these variables explained 71% of the dependent variable’s variance, which is considered substantial. Overall, it makes it easier for firms in the software sector to use Blockchain technology, which would increase the overall competitiveness of Malaysia’s software sector in the international market.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Blockchain Fostering Sustainability: Challenges and Perspectives)
Open AccessArticle
Optimization of Cascade Small Hydropower Station Operation in the Jianhe River Basin Using a One-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Model
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12138; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612138 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hydropower development brings benefits in terms of power generation and flood control, but it also has inevitable ecological impacts. These impacts must be considered and addressed in order to ensure sustainable development and minimize harm to the environment. This study utilized the MIKE
[...] Read more.
Hydropower development brings benefits in terms of power generation and flood control, but it also has inevitable ecological impacts. These impacts must be considered and addressed in order to ensure sustainable development and minimize harm to the environment. This study utilized the MIKE 11 HD modeling system to construct a hydrological and hydrodynamic model of the Jianhe River basin. The model incorporates the flow demand of ecologically sensitive targets for scheduling purposes and was calibrated and validated using hydrological data from 2014 to 2022. The hydrodynamic model was then applied to analyze the evolution characteristics of the water level in the main stream of the Jianhe River, identify key areas and periods for hydropower station operation, and calculate the minimum ecological water requirement using verification and estimation methods. Based on these findings, an ecological dispatching scheme for the cascade hydropower stations in the Jianhe River basin was developed. The results demonstrate satisfactory performance of the constructed NAM model for rainfall runoff and the 1D hydrodynamic MIKE 11 HD model for the Jianhe River basin. The deterministic coefficients exceed 0.8, and the relative errors in the total water volume are below 5.5%. The critical time and space interval for hydropower station operation in the main stream of the Jianhe River is identified as December to February of the following year, with the highest risk of flow interruption occurring in January, primarily concentrated between the Duoluo II and Huahai hydropower stations. If the appropriate dispatching scheme is not implemented in the areas prone to flow interruption during critical periods, it will have a negative impact on the ecological environment. These findings provide a scientific basis and decision support for developing multi-objective ecological flow guarantee schemes for rivers.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Quantitative Evaluation Model for the Seismic Resilience of Water Supply Systems Based on Fragility Analysis
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12137; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612137 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
A quantitative evaluation model is proposed to assess the seismic resilience of water supply systems. The water supply system is divided into three parts: water sources, aboveground infrastructures, and underground pipeline network, and importance factors for the different parts are quantified. Resilience demand
[...] Read more.
A quantitative evaluation model is proposed to assess the seismic resilience of water supply systems. The water supply system is divided into three parts: water sources, aboveground infrastructures, and underground pipeline network, and importance factors for the different parts are quantified. Resilience demand is expressed as the desirable functionality loss and the recovery time of the water supply system after an earthquake. First, seismic fragility models are established for the different components of the water supply system. A water quality index is utilized to represent the impact of earthquakes on the water sources, the seismic performances of aboveground infrastructures are represented by fragility curves, and the repair rate in terms of number of repairs per kilometer is adopted for the pipeline network. Then, the post-earthquake functionality of the water supply system is quantified based on seismic fragility analysis. Changes in the water quality index are used to indicate the functionality losses related to water sources, the functionality losses of aboveground infrastructures are represented by the economic losses derived from component fragility curves, and post-earthquake functionality losses in the underground pipeline network are quantified by hydraulic simulations. The functionalities of the three parts are calculated separately, and then the overall system functionalities are obtained as the sum of the weighted functionalities of the three parts. Finally, a repair strategy is developed and the recovery time is calculated considering the system damage scenarios, system functionality analyses, and resource reserves. The proposed resilience assessment model considers all components of the water supply system, and the results are reliable when the basic information is complete and accurate.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Urban Resilience and Critical Infrastructure)
►▼
Show Figures
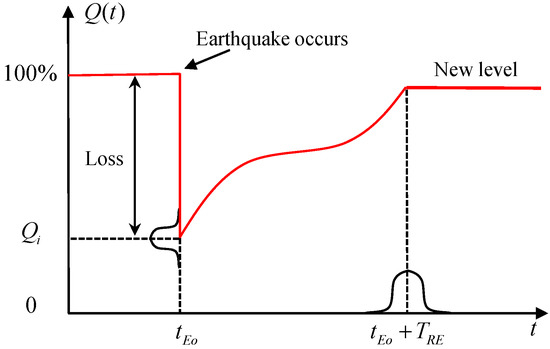
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Can Mergers and Acquisitions Promote Technological Innovation in the New Energy Industry? An Empirical Analysis Based on China’s Lithium Battery Industry
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12136; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612136 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The advancement of technological capabilities within lithium battery enterprises crucially facilitates the high-quality development of the new energy industry. This study aims to empirically investigate the impact of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) on the technological innovation capacities of these enterprises, with a specific
[...] Read more.
The advancement of technological capabilities within lithium battery enterprises crucially facilitates the high-quality development of the new energy industry. This study aims to empirically investigate the impact of mergers and acquisitions (M&A) on the technological innovation capacities of these enterprises, with a specific focus on the lithium battery sector in China. Utilizing data from 34 publicly listed companies spanning the period from 2012 to 2022, we employ the multi-period double-difference method for comprehensive analysis. Researchers have observed that the implementation of merger and acquisition (M&A) strategies by new energy companies leads to an approximately 1.5 percentage point increase in their technological innovation level. However, the improvement in the green technological innovation level is not significant. After a series of robustness tests, the aforementioned conclusion remains valid. Additionally, with the enhancement of firms’ knowledge absorption capacity and regional intellectual property protection, M&A activities can further promote technological innovation in new energy companies and contribute to the enhancement of green technological innovation. Heterogeneity analysis has revealed that technological M&A crucially facilitates the improvement of technological innovation levels among listed companies in the lithium battery industry. Implementing M&A strategies not only benefits the enhancement of firms’ technological innovation levels but also significantly fosters green technological innovation. Furthermore, further research has indicated that changes in the level of green technological innovation after the implementation of M&A strategies by new energy companies facilitate the reduction of industrial wastewater and sulfur dioxide emissions. The main innovation of this study, which utilizes new energy companies as the research object, is as follows: it reveals the causal relationship and regulatory mechanism between M&A, technological innovation, and green technological innovation in new energy companies. Furthermore, the study analyzes the mechanism that promotes green technological innovation in new energy companies from the intellectual property protection perspective. Moreover, it assesses the heterogeneous impacts of changes in both technological innovation levels and green technological innovation levels on environmental governance after the implementation of M&A activities.
Full article
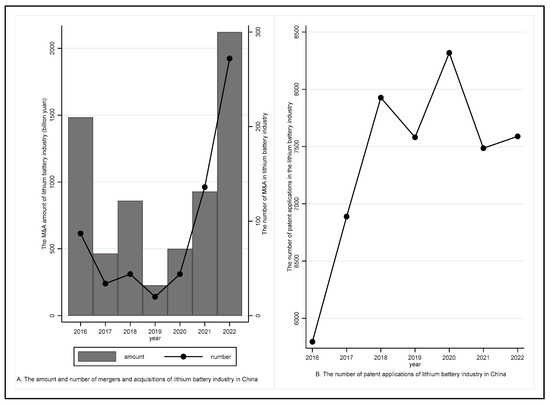
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
CO2 Emissions from Plastic Consumption Behaviors in Thailand
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12135; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612135 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Plastic waste is an environmental crisis that is becoming increasingly well-documented. The rapid expansion of plastic manufacturing and consumption has led to a harmful cycle of pollution and greenhouse gas emissions due to petroleum-based production and plastic waste disposal. Plastic production and disposal
[...] Read more.
Plastic waste is an environmental crisis that is becoming increasingly well-documented. The rapid expansion of plastic manufacturing and consumption has led to a harmful cycle of pollution and greenhouse gas emissions due to petroleum-based production and plastic waste disposal. Plastic production and disposal depend on the consumption behavior of people. This study aimed to examine the plastic consumption behavior in Thailand and its impact on climate change at the end-of-life stage. The general information, plastic consumption, and plastic waste management were collected via questionnaires for each product lifetime, including single-use, medium-use, and long-use plastics. Based on 567 questionnaires, the results showed that people consumed single-use plastic, e.g., plastic bag, food container, cutlery, straws, and bottles, at a rate of about nine pieces/household/day or three pieces/cap/day. The medium-use and long-use plastic were 10 pieces/household/month and 50 pieces/household/year, respectively. It should be remarked that population density, education, and number of household members affected plastic consumption behavior, especially for single-use plastic. Regarding the disposal of end-of-life plastics, Thai people, on average, contribute 0.15 kg CO2eq/household/day to climate change. Many households have mismanaged waste by open dumping and open burning. Therefore, practicing proper waste management will help Thailand on the path to carbon neutrality in the future.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Climate Change and Environmental Sustainability, 2nd Volume)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Reconstruction of Fault Architecture in the Natural Thermal Spring Area of Daruvar Hydrothermal System Using Surface Geophysical Investigations (Croatia)
by
, , , , , , and
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12134; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612134 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The sustainable utilization of geothermal energy mostly depends on the characteristics of the geothermal resource from which it is extracted. Among others, detailed geological modeling is a key factor for estimating the potential of a geothermal resource. This research focuses on the modeling
[...] Read more.
The sustainable utilization of geothermal energy mostly depends on the characteristics of the geothermal resource from which it is extracted. Among others, detailed geological modeling is a key factor for estimating the potential of a geothermal resource. This research focuses on the modeling and reconstruction of the geological setting of the Daruvar thermal spring area using geophysical techniques. An integrated geophysical approach based on electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and both active and passive seismic (MASW and HVSR) methods was used. Based on ERT results and the stratigraphic logs of the wells in Daruvar, three resistivity layers/geological units were identified. The deepest layer with resistivity < 150 Ωm is the Triassic carbonate that constitutes the thermal aquifer. Sharp lateral variations in the resistivity distributions within the bedrock were interpreted as fault damage zones saturated with thermal waters. Integrating the results of the seismic methods, the thickness of the first seismic layer that corresponds to the Quaternary cover was estimated from 5 to 20 m. Here, results of the geophysical investigations were combined into a 3D geological model highlighting the occurrence of subvertical N-S and E-W trending faults in the Daruvar spring area. The N-S-trending fault was interpreted as a fault plane parallel to the regionally mapped Daruvar fault. This fault juxtaposes the Triassic carbonate complex of the thermal aquifer with a Neogene sedimentary sequence of significantly lower permeability. Neogene–Quaternary tectonic activity further increased the fracturing and the permeability field in the Daruvar spring area, as proven by the smaller scale E-W faults and the well logs. This fracture network permits a quick upwelling of thermal fluids resulting in thermal springs with temperatures up to 50 °C. This work proves that the construction of a detailed geological model is crucial for assessing the reservoir and fault geometries in thermal systems hosted in fractured carbonate rocks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Groundwater Protection and Sustainable Utilization)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Sustainable Rainwater Management and Life Cycle Assessment: Challenges and Perspectives
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12133; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612133 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
Rainwater harvesting is a promising technique for more rational water use. However, its sustainability merits remain a subject of ongoing debate among researchers. Life cycle assessment (LCA), a method employed to measure the environmental impact of varying solutions, is helpful in this regard.
[...] Read more.
Rainwater harvesting is a promising technique for more rational water use. However, its sustainability merits remain a subject of ongoing debate among researchers. Life cycle assessment (LCA), a method employed to measure the environmental impact of varying solutions, is helpful in this regard. Accordingly, this paper delivers an integrative review based on the PRISMA protocol, outlining challenges and potential avenues for the LCA application to rainwater harvesting. The central findings indicate that while residential buildings are most commonly examined, more consensus is needed on a uniform analytical framework. Furthermore, several benefits of rainwater are often not considered in LCA and need further exploration to understand possible synergies for its broader implementation. Finally, LCA integration with a life cycle cost assessment (LCCA) shows exciting results as it may be a more straightforward showcase of the benefits of an integrated assessment. It is concluded that specific details of the LCA of rainwater harvesting may still be simplistic. There is much work to be done in holistic assessments to prove the system’s sustainability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Rainwater Management: Challenges and Perspectives)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Food Safety and Nutrition Knowledge on the Lifestyle of Young Poles—The Case of the Lublin Region
by
, , , , , , and
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12132; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612132 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The aim of the study was to show the differences in healthy lifestyle and healthy food choices between high school and college students. The study was conducted in the Lublin region, Poland, with a group of 200 high school and college students using
[...] Read more.
The aim of the study was to show the differences in healthy lifestyle and healthy food choices between high school and college students. The study was conducted in the Lublin region, Poland, with a group of 200 high school and college students using purposive sampling with the following four subgroups of 50 students, broken down by gender and type of school. Respondents completed a questionnaire concerning healthy lifestyle, healthy food choices, and barriers preventing a healthy lifestyle. Using discriminant analysis, the factors and barriers to practicing a healthy lifestyle and the factors of healthy food choices were identified by the respondent group and by gender. A multidimensional exploratory technique was also used to interpret the results. The surveyed high school and college students were not very committed to practicing a healthy lifestyle. Multidimensional exploratory technique was also used to interpret the lifestyle and healthy food choices questions. There was variation between the attitudes of college and high school students toward a healthy lifestyle. High school students paid more attention to physical activity and eating breakfast than did college students. On the other hand, college students, at a greater level than high school students, ate a healthy diet and checked the composition of the products they consumed, including the presence of preservatives and artificial additives, and the expiration date of the products. The main barriers to practicing a healthy lifestyle were, for college students, a lack of time and, for high school students, a lack of healthy food offerings in high school canteens.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Healthy Eating and Sustainable Consumption in Foodservice Industry)
►▼
Show Figures
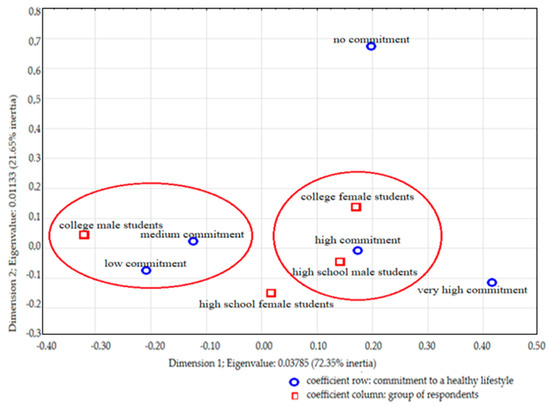
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Analysis of Hotspot Stress Endurance in Pristine and Thermal Cycled Prestressed Glass–Glass Photovoltaic Modules
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12131; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612131 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Hotspots pose a significant long-term reliability challenge in photovoltaic (PV) modules that can have a detrimental impact on the efficiency, safety, and financial viability of a PV system. This paper aims to evaluate the endurance of hotspot stress in pristine and prestressed glass–glass
[...] Read more.
Hotspots pose a significant long-term reliability challenge in photovoltaic (PV) modules that can have a detrimental impact on the efficiency, safety, and financial viability of a PV system. This paper aims to evaluate the endurance of hotspot stress in pristine and prestressed glass–glass (GG) modules. The accelerated prestressing was conducted for 600 thermal cycles (TC600) to represent decades of field exposure. GG modules are quickly becoming an alternative to the traditional glass–backsheet (GB) modules that have been the industry standard. Unlike other conventional studies that subject only pristine modules to hotspot stress, this paper evaluates the performance of an accelerated/simulated field-aged GG module (using TC600) and a pristine GG module. Pre- and post-characterizations were performed before and after each test to determine changes in electrical performance and observe any defects in GG modules. During the hotspot test, an approximately 200 °C maximum cell temperature was observed with a cell shading of 25% (the worst-case shading ratio). After the hotspot test, electroluminescence imaging indicated that most cells in the prestressed GG module exhibited severe damage whereas no significant defects were evident in the pristine GG module where the prestressed GG module degraded 8.2% and the pristine GG module degraded 1.5% in maximum power. These findings are critical for the industry, considering that GG bifacial modules will dominate the market.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Application of Flexible Tools in Magnesia Sector: The Case of Grecian Magnesite
by
, , , , and
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12130; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612130 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this paper, two flexible model tools (CO2 emissions/cost tool and CFD tool) that simulate the production process of Grecian Magnesite (GM) and extract economic and technical conclusions regarding the substitution of fossil fuels with various types of biomass are presented and
[...] Read more.
In this paper, two flexible model tools (CO2 emissions/cost tool and CFD tool) that simulate the production process of Grecian Magnesite (GM) and extract economic and technical conclusions regarding the substitution of fossil fuels with various types of biomass are presented and analyzed. According to the analysis, the higher the substitution, the higher the profit in both CO2 emissions and cost reduction. The reduction in CO2 emissions that can be achieved through biomass fuel substitution ranges from 15% for a 30% substitution to 35% for a 70% substitution. Accordingly, production costs are also reduced with the use of biomass. The initial results of this decision-making cost tool showed that the most profitable solution is a 70% substitution, for which production costs can be reduced by up to 38.7%, while the most beneficial type of biomass proved to be the olive kernel. A proposed and feasible solution is the substitution of 50% sunflower husk pellets, which will result in a reduction of 25% in CO2 emissions and almost 10% in production cost. From CFD simulation, a reduced order model (ROM) has been developed that allows the running of scenarios in real time, instead of the usual long times required by complex simulations. Comparative studies of fuel blend and biomass type can be carried out easily and rapidly, allowing one to choose the most suitable substitution.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainability in Biomass and Waste Fuels Utilization)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of the Energy Performance of a Retrofitted Low-Rise Residential Building after an Energy Audit
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12129; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612129 - 08 Aug 2023
Abstract
The main reason for this research is to support the Korean government building retrofitting program initiated to evaluate energy usage trends, propose energy-saving technologies, and focus on reducing the energy demand in residential buildings through energy efficiency improvement. This is achieved by assessing
[...] Read more.
The main reason for this research is to support the Korean government building retrofitting program initiated to evaluate energy usage trends, propose energy-saving technologies, and focus on reducing the energy demand in residential buildings through energy efficiency improvement. This is achieved by assessing the energy saved after introducing a simple retrofitting measure to an existing residential building. The energy savings in the building were realized after collecting relevant data from the house occupants, analyzing electricity bills, and introducing energy conservation measures (ECMS), leading to an improvement in the energy performance of the building. The building envelope saved 2098 kWh and 6307 kWh of energy via the heating and cooling equipment with an initial incremental cost of USD 500, fuel cost savings of USD 306, and a simple payback of 1.6 years. The analysis takes the occupants 2.6 years to recoup the initial cost of USD 2400 invested with an electricity savings of 2144 kWh. Also, 3.3 tons of CO2 emissions per year were reduced, equivalent to 3.3 people reducing energy use by 20%. Finally, the actual and simulated data are almost the same for the consumption period, with only a slight difference in October and December, given 0.92 as the Pearson Correlation coefficients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Prospective Pathways to Architectural and Urban Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Sustainability Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Agriculture, AgriEngineering, Energies, Sustainability, Water
Emerging Agricultural Engineering Sciences, Technologies, and Applications
Topic Editors: Muhammad Sultan, Yuguang Zhou, Redmond R. Shamshiri, Muhammad ImranDeadline: 31 August 2023
Topic in
Machines, Micromachines, Remote Sensing, Sustainability, Symmetry, Wind
Energy Equipment and Condition Monitoring
Topic Editors: Zhifeng Xiao, Bin Huang, Lida LiaoDeadline: 15 September 2023
Topic in
Batteries, Designs, Energies, Materials, Sustainability
Materials for Energy Harvesting and Storage
Topic Editors: Xia Lu, Xueyi LuDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Buildings, COVID, Energies, Environments, IJERPH, Sustainability
Advanced Ventilation in and beyond the COVID-19 Pandemic
Topic Editors: John Z Lin, Zhaosong Fang, Sheng Zhang, Jian Liu, Yong Cheng, Chao HuanDeadline: 20 October 2023

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Sustainable E-learning and Education with Intelligence
Guest Editor: Hao-Chiang Koong LinDeadline: 12 August 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Sustainable Supply Chain Innovation and Operation Management
Guest Editors: Lei Xu, Xiaochen Sun, Guihong Zhao, Xiaohang YueDeadline: 15 August 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Characteristics, Health Risk Assessment and Sustainable Management of Air Pollutants in Asia
Guest Editors: Fei Li, Dingyi Wang, Hongtao YiDeadline: 31 August 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Human–River Interactions in Cities
Guest Editors: G. Mathias Kondolf, Amir Gohar, Yves-François Le LayDeadline: 15 September 2023
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Eutrophication and Sustainable Management of Water
Collection Editor: Marco Ragazzi
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Power System and Sustainability
Collection Editors: Gaetano Zizzo, Favuzza Salvatore
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Marketing and Sustainability
Collection Editor: Colin Michael Hall
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Teacher Professional Development in ESD
Collection Editor: Michele Biasutti